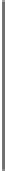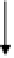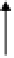Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Interfacial Complexation
Solution Complexation
membrane
aqueous
aqueous
aqueous
membrane
aqueous
HA
HA
HA
HA
HA
HA
H
i
+
H
i
+
H
o
+
H
o
+
A
-
A
-
A
-
A
-
A
-
A
-
Figure 6. The sketch map of uncoupling process of protonophores. HA: protonated uncoupler; A
-
:
deprotonated uncoupler; H
o
+
, H
i
+
: protons in the outer and inner bulk phase, respectively [58].
OH
OH
OH
OH
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
NO
2
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
NO
2
PCP
TCP
DNP
DCP
Cl
OH
O
NC
N
C
N
CF
3
Cl
H
Cl
NC
Cl
TCS
FCCP
Figure 7. Structures of some representative weakly acidic uncouplers.
Table 2. Inhibitory compounds of oxidative phosphorylation [66,67]
Compounds
Effects on oxidative phosphorylation
Rotenone, Amytal
Inhibit electron transfer from Complex I at quinine-binding site
Antimycin A
Inhibit the electron transfer activity of ubiquinol-cytochrome c
oxidoreductase
Cyanide, CO, Azide
Inhibit electron transfer to oxygen, preventing the reduction of
oxygen
2,4-dinitrophenol,
Pentachlorophenol
Disrupt the proton gradient by carrying protons across the membrane
Oligomycin, DCCD
Inhibit ATP synthase by blocking the flow of protons through proton
channel F
0