Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
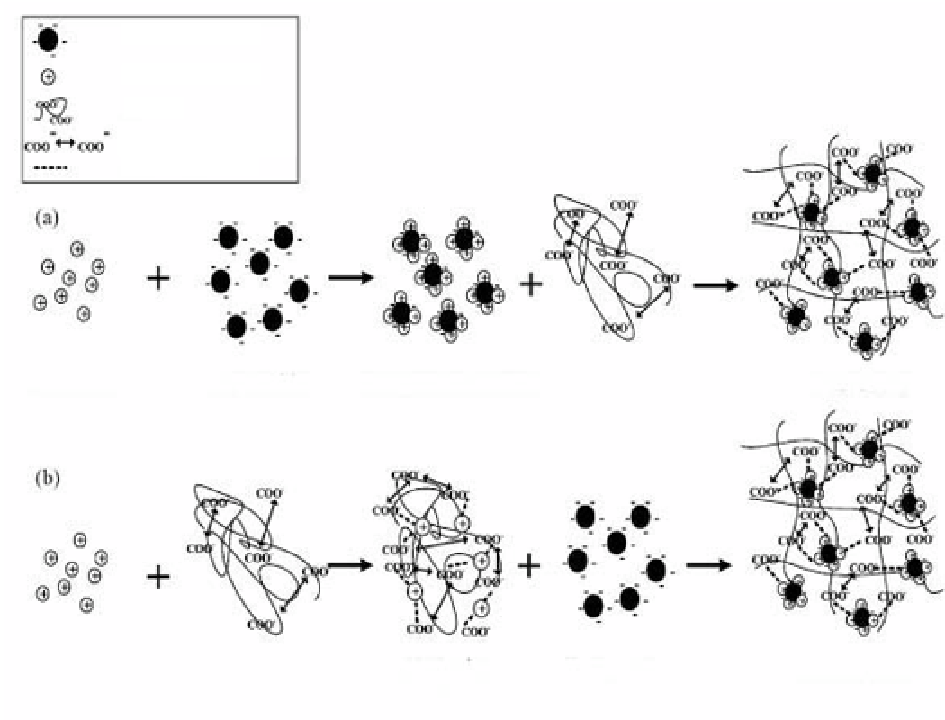
Kaolin particle
Metal cation
γ
-PGA
Electrostatic repulsion
Attractive force
Metal cations
+
kaolin particles
Metal cations
+
γ
-PGA
Metal cations
Kaolin particles
Bridging (Floc)
Metal cations
Kaolin particles
Bridging (Floc)
γ
-PGA
Metal cations
+
γ
-PGA
Source
: Wu and Ye 2007.
Figure 7. Proposed mechanism of flocculation by γ-PGA.
4.
γ
-PGA as an Adsorbent of Cationic Dyes
Cationic dyes are the brightest class of soluble dyes used by the textile industry and the
waste discharge accumulates heavy organic load in the environment causing a harmful impact
on both aquatic organisms and human [60-64]. Because of the limitations prevailing in the
conventional treatment methods [62], there has been a continuous search for a safe, eco-
friendly and biodegradable adsorbent to treat dye-containing wastewaters. Lately, the
bioremediation of dyes employing extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) produced by
microorganisms is gaining attention [65-69], and this part of the chapter consolidates the
published reports on evaluating γ-PGA as an adsorbent of cationic dyes. In all the three
studies reported here [27,70,71], the γ-PGA (H-form; MW 990 kDa) produced from
B.
subtilis
by salvage bioconversion pathway was employed. Figure 8 presents the molecular
structure of cationic dyes studied along with their color index name, color index classification
number, formula weight and wavelength of maximum absorption (λ
max
).