Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Scenario 1
Scenario 2
Scenario 3
Scenario4
Scenario 5
Scenario 6
Workflow 5
Workflow 3
Workflow 1
DC
analysis
Sample
treatment
File_Conversion
Workflow 2
Workflow 4
Material
analysis
Quality
control
Fig. 7.6
The workflow bus allow the execution of application workflows across multiple SWMS.
The runtime behavior of a legacy workflow is modeled as a scenario. The scenarios of legacy
workflows are coupled through a meta-workflow. At runtime, an administrator agent manages the
delivery of information between the scenarios
applications, by providing interoperability and flexibility in a large-scale distrib-
uted environment. Through the use of XML-based protocols (SOAP) and inter-
faces (WSDL), web services can expose the entirety or selected parts of any
application in a language-independent fashion across heterogeneous platforms.
Moreover, these features enable them to be combined in a workflow so that more
complex operations may be achieved (Zhang et al.
2006
) . Currently, two
approaches apply to workflow implementations: Service Orchestration and
Service Choreography.
In Service Orchestration the process is always controlled by a workflow engine,
so all invocations (and replies) are made by (and to) that workflow. On the other
hand, choreography is more collaborative, because it describes the message exchange
among interacting, yet independent web services.
9
Regardless of the architecture
chosen, any workflow implementation is faced with a data transport problem which
can be summarized in the following way: (1) In service orchestration, all data go
through the workflow engine before being delivered to a consuming web service.
This practice not only makes data delivery inefficient, but also causes failures in
workflow execution due to the data burden workflow engines have to carry. (2) Data
transfers are made through SOAP, a protocol unfit for large-scale data transfers
(Daly et al.
2005
). Curing data through SOAP is problematic for many scientific
applications, since the success of the paradigm has caused an abundance of web
services to be deployed. As applications started to produce more data, these services
fail to scale with the increased data demands. (3) Third-party file transfer is suitable
for transferring large data sets, but is restricted to files. This results in unnecessary
intermediate transfers that slow down workflow execution and place excessive
demands on storage resources.
9
Web Service Choreography Interface:

























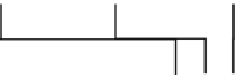


Search WWH ::

Custom Search