Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
120
Initial effective stress
100
80
Excesspore
water
pressure
(kPa)
Mountain
sandy soils
60
40
Cement-stabilized
20
Fiber-cement
stabilized
0
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
Elapsed time (sec)
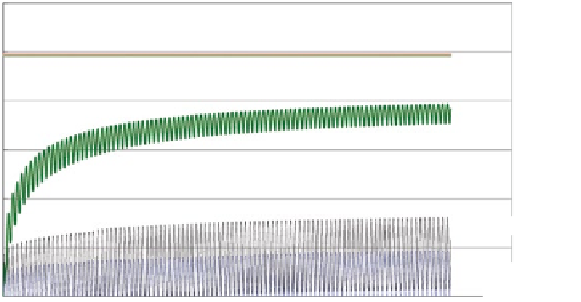
Fig. 10.7
Cyclic tri-axial compression test results
10.2.6
Construction Case Studies
10.2.6.1
Technology for Using High Moisture Content Soil in Embankment
Construction for the Hamao Basin Embankment Work (Tohoku
Regional Bureau of the Ministry of Land Infrastructure and
Transport (MLIT), Fukushima River National Highway Office)
The Tohoku Regional Bureau of MLIT proposed to use private company technolo-
gies and patents in construction projects to achieve cost-reductions and increase the
rate of recycling and in fiscal year 2002, selected four technologies towards this
objective. One of these technologies was the fiber-solidification method for using
high moisture content soils in embankment construction, and this was employed
at Sukagawa town, Fukushima Prefecture, in the Hamao river basin construction
project. This construction in the Hamao area of the Abukuma river catchment is
to protect downstream areas from flood damage. In addition to factors of duration,
cost and feasibility when excavating the retarding basin, the soil excavated would
also be used in the construction of the levee around the basin, requiring an effective
technology to make economic use of high water content muds. In the Fiscal 2002
year construction, 3000 m
3
were processed by the fiber-solidified soil method and
used on the embankment building work. Subsequently, the embankment suffered no
erosion from rain, nor have any cracks appeared in the bank, showing again that the
fiber-solidified soils have high-durability, and that this was highly suitable for this
type of project (Fig.
10.8
).