Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
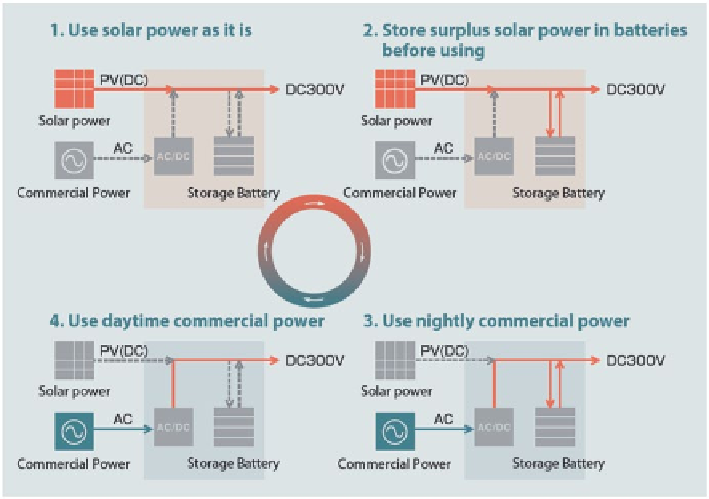
Fig. 7.4
Energy Options and control. (GSES
2012
)
7.2.5
Energy Management System (EMS) and Visualisation
The basic principle of the energy management system is shown in Fig.
7.4
, whereby
the ideal balance is set between available renewable energy and back up commer-
cial power.
The energy supply and consumption and other basic information on the system
is collected and processed via the EMS. The basic data collected and analyses con-
ducted are shown in Fig.
7.5
and a reproduction of the actual display examples in
Fig.
7.6
. By visualizing the flow of electricity in real-time and by using animations,
it is possible to provide an intuitive understanding of the situation, and by providing
energy-saving advice for the situation depicted on the same screen, it is possible to
encourage appropriate energy saving action. Consumption and results of energy-
saving activities, and energy saving ratios for each floor are calculated, compared
and displayed, thus raising energy-saving awareness.
7.2.6
Smart Building and Energy System Aspects
The actual schematic of the main building and the associated additional services
such as a charging point for an electric vehicle are shown in Fig.
7.7
. The concept
is to use both AC power supply from the public grid and local DC power supply of
natural energy. Both the commercial electricity and renewable energy can be used
independently; moreover energy can be saved by a combination of IT and the DC