Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 7.1
Battery specifications
Battery type
Lithium ion secondary battery
Storage capacity
57.6 kWh (8 units of 7.2 kWh)
Rated input
PV48 kW, AC48 kW
Rated output
48 kW
Rated voltage
307.2 V
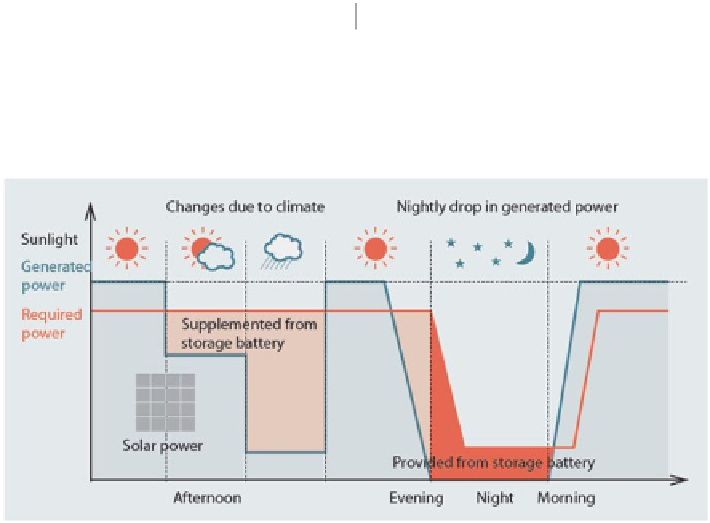
Fig. 7.2
Daily adjustments of flows to and from the batteries to stabilize power provision. (GSES
2012
)
In the above configuration, we have applied current technology to connect small
sources of renewable energy with a secondary battery system, as well as the ef-
fective fusion/collaboration between locally- produced household energy creation
and the usage of public commercial sources of electricity. The system also needs
to include balancing controls to reflect the fluctuations in power supply depending
on the time of day, season and weather. When the weather is poor and not enough
solar power is generated for consumption, the shortfall can be compensated for by
electricity supplied from the storage battery to stabilize power provision. Power can
also be provided from the lithium-ion storage batteries for a certain amount of time
at night or during power failure. An illustration of the daily fluctuations and adjust-
ment of the power flow to and from the batteries is in Fig.
7.2
.
7.2.4
DC Circuitry and Lighting
When the usual household electrical system is considered, there are many cases
where the AC of the supply has to be converted to DC in order to use the elec-
tricity—typical examples being mobile devices, computers, and some digital TVs.
Thus if we are considering the original source starting as DC, the traditional system
wastes energy on 2 conversions—first from the DC supply from the PV solar to the