Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
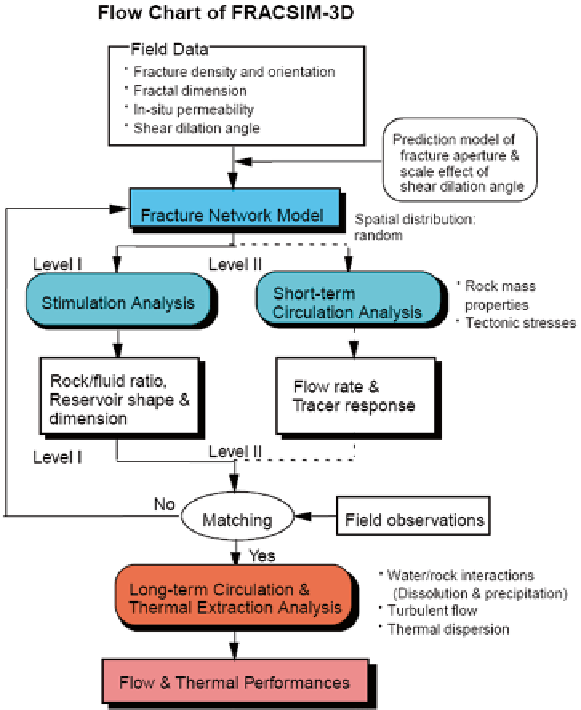
of the fractures to be generated in the calculation volume. To conduct fluid flow
analysis for hydraulic stimulation and to determine the water pressure within the
fractures, the generated fractal fracture network is mapped on a regular cubical grid.
Then the equivalent permeability of each block is calculated, based on the sum of
the products of the fracture apertures to the 3rd power and length of the intersection
of the fracture with the block face. The flow analysis is performed assuming that the
calculated permeability controls the fluid flow rate from one block to another block.
In FRACSIM-3D, shear dilation mechanism for fracture opening is accounted for,
in addition to jacking mechanisms. The fractal nature of the fracture surface rough-
ness is also taken into account in order to predict the shear dilation of fractures. This
grid model with a spatial distribution of equivalent permeability is employed to
perform numerical computations for mass and heat transfer and to simulate the ar-
tificial reservoir formation by hydraulic stimulation and subsequent heat extraction
through the man-made water circulation loop in the reservoir. The model can also
Fig. 6.11
Design methodology for engineered geothermal reservoirs