Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
Systems with more efficient power supplies consume on average from 15% to 30% less power than
conventional designs. This can result in a significant energy and cost savings over the life of a system.
In addition, the resulting lower heat output both improves system reliability and saves additional
energy in cooling the system as well as the surrounding environment.
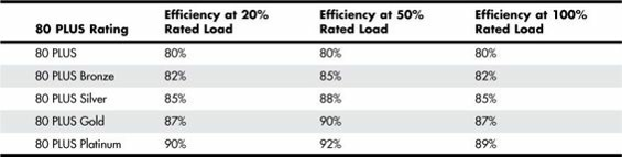
The 80 PLUS program currently has five levels of certification, from 80 PLUS to 80 PLUS Platinum.
Each level of certification signifies different minimum levels of efficiency, which are measured at
three different loads (20%, 50%, and 100%).
Table 18.26
shows the details of each of the
certification levels.
Table 18.26. 80 PLUS Certification Levels
How is this efficiency determined, and what is the overall effect? The PSU in a PC converts the high
voltage (120V in the USA) AC wall current to 12V and lower DC voltages for use in the PC.
Unfortunately, no PSU is 100% efficient, meaning that some of the power is lost or used up during the
conversion and ends up being dissipated as heat. Conventional PSUs are or were normally about 70%
efficient, which means that 30% of the energy drawn from the wall socket is wasted and ends up as
heat. As an example, let's take a system that draws 250 watts total.
Table 18.27
shows the resulting
AC power draw and the amount of wasted energy if the PSU were 70%, 80%, or 90% efficient.
Table 18.27. The Effect of PSU Efficiency on AC Power Draw and Wasted Energy
As you can see, when supplying the same 250 watts of power to the system, the actual amount of
power used, and consequently the amount of energy wasted, varies considerably. A more efficient
PSU can save a tremendous amount of energy and money over the life of a system. Because of this, I
highly recommend 80 PLUS certified power supplies, especially those earning the higher efficiency
ratings.
ENERGY STAR
ENERGY STAR is an international standard for energy-efficient consumer products, including
computers and power supplies. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) introduced
ENERGY STAR as a voluntary labeling program designed to identify and promote energy-efficient
products. The first products labeled in the program were computers and monitors. In the years since,
ENERGY STAR has become an international standard, and the label can be found on new homes,
commercial and industrial buildings, appliances, office equipment, lighting, electronics, and more.