Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
the design, it could either shut down or operate in a reduced functionality mode.
Due to special keying on the 8-pin connector, it cannot be plugged into a 6-pin socket. Because of
this, many power supply manufacturers include 8-pin connectors made in a “6+2” arrangement, where
the portion containing the two extra pins can be disconnected, leaving a 6-pin connector that will, of
course, work in a 6-pin socket.
Caution
The 8-pin PCI Express Auxiliary Power Connector and the 8-pin EPS12V CPU Power
Connector use similar Molex Mini-Fit Jr. connector housings. Although they are keyed
differently, the keying can be overcome by sufficient force such that you can plug an EPS12V
power connector into a graphics card, or a PCI Express power connector into a motherboard.
Either of these scenarios results in +12V being directly shorted to ground, potentially
destroying the motherboard, graphics card, or power supply.
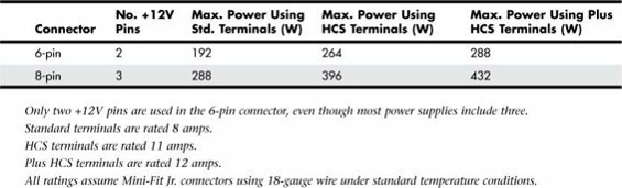
The 6-pin connector uses two +12V wires to carry up to 75W, whereas the 8-pin connector uses three
+12V wires to carry up to 150W. Although these figures are what the specifications allow, the wires
and terminals of each connector are technically capable of handling much more power. Each pin in
the PCI Express auxiliary power connectors is rated to handle up to 8 amps of current using standard
terminals—more if using HCS or Plus HCS terminals. By counting the number of terminals, you can
calculate the power-handling capability of the connector (see
Table 18.22
).
Table 18.22. PCI Express Graphics Power Connector Maximum Power-Handling Capabilities
Even though the specification allows for a delivery capability of 75W (6-pin connector) or 150 watts
(8-pin connector), the total power-handling capacity of these connectors is at least 192 and 288 watts,
respectively, using standard terminals, and even more using the HCS or Plus HCS terminals.
These two auxiliary power connectors are sometimes called PCI Express Graphics (PEG), Scalable
Link Interface (SLI), or CrossFire power connectors because they are used by high-end PCI Express
boards with SLI or CrossFire capabilities. SLI and CrossFire are NVIDIA and AMD's methods of
using two video cards in unison, with each one drawing half of the screen for twice the performance.
Each card can draw hundreds of watts, with many of the high-end cards using two or three auxiliary
power connectors. This means that most power supplies that are rated as SLI- or CrossFireX-ready
include at least two or more of the 6/8-pin PCI Express graphics power connectors. Using two video
cards drawing 300 watts each means that even if you have a 750-watt power supply, you will have
only 150 watts of power left to run the motherboard, processor, and all the disk drives. With high-
powered processors drawing 130 watts or more, this may not be enough. For this reason, systems
using two or more high-end video cards require the highest-output supplies available, and some of the