Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
allows for a maximum supply of approximately 250 watts to the motherboard. Because motherboards
with high-speed processors and multiple cards installed could draw more power than that and power
supply manufacturers were building supplies with 300-watt and higher ratings, melted connectors
were becoming more and more common. The terminals in the main connector overheated under such a
load.
To allow for additional power from the supply to the motherboard, Intel modified the ATX
specification to add a second auxiliary power connector for high power-drawing ATX motherboards
and 250-watt or higher rated supplies. The criteria is such that, if the motherboard could draw more
than 18A of +3.3V power or more than 24A of +5V power, the auxiliary connector is required to
carry the additional load. These higher levels of power are needed in systems using 250- or 300-watt
or greater supplies.
The 6-pin auxiliary power connector was added as a safety or stopgap measure in the ATX
motherboard 2.02/2.03 and ATX12V 1.x power supply specifications for systems in which the +3.3V
and +5V power draw could exceed the respective 18A and 24A maximums allowed using only the
main connector with standard terminals. These conditions would normally be met in systems
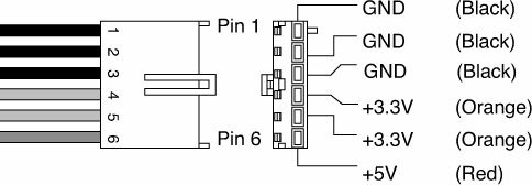
requiring 300W or higher output power supplies. The auxiliary power connector is a 6-pin Molex
90331-0010 connector, which is similar to the motherboard power connectors used on older AT/LPX
power supplies for Baby-AT motherboards (see
Figure 18.23
).
Figure 18.23. ATX 2.02/2.03 and ATX12V 1.x auxiliary power connector, side and terminal end
view.
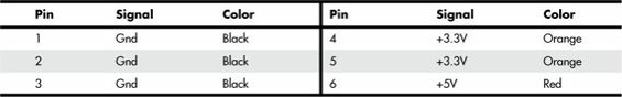
The pinouts of the auxiliary connector are shown in
Table 18.8
.
Table 18.8. ATX Auxiliary Power Connector Pinout
Each terminal in the auxiliary power connector is rated to handle up to 5 amps of current, slightly less
than the main power connector. By counting the number of terminals for each voltage level, you can
calculate the power-handling capability of the connector, as shown in
Table 18.9
.
Table 18.9. Six-Pin Auxiliary Power Connector Maximum Power-Handling Capabilities