Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
and might be compatible with other brands of devices that are also Bluetooth enabled. The only
drawback I've seen with Bluetooth-based devices is that they usually consume more power, resulting
in shorter battery life, and the configuration or pairing of the device and transceiver can be more
difficult than those using proprietary wireless technology.
For more information about Bluetooth, see
Chapter 17
, “
Local Area Networking
,
”
p.
799
.
Power Management Features of Wireless Input Devices
A wireless mouse is useless if its batteries fail, so several vendors of wireless products have
developed sophisticated power-management features to help preserve battery life—especially with
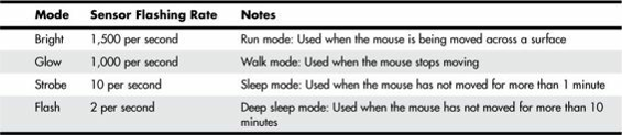
optical mice, which use power-eating LEDs to illuminate the mousing surface. For example, Logitech
Cordless mice have four operating modes, as shown in
Table 15.3
.
Table 15.3. Logitech Cordless Mouse Optical Power Management
Wireless keyboards are activated only when you press a key or use the scroll wheel available on
some models, so they tend to have longer battery lives than mice. Conventional ball-type mice also
have longer battery lives than optical mice, but ball-type mice have largely been discontinued, as the
convenience and accuracy of optical mice outweigh battery-life issues for most users.
Troubleshooting Wireless Input Devices
If your wireless input device does not work, check the following:
•
Battery failure
—The transceivers attached to the computer are powered by the computer, but
the input devices themselves are battery powered. Check the battery life suggestions published
by the vendor; if your unit isn't running as long as it should, try using a better brand of battery or
turning off the device if possible.
•
Lost synchronization between device and transceiver
—Both the device and the transceiver
must be using the same frequency to communicate. Depending on the device, you might be able
to resynchronize the device and transceiver by pressing a button, or you might need to remove
the battery, reinsert the battery, and wait for several minutes to reestablish contact.
•
Interference between units
—Check the transmission range of the transceivers in your
wireless units and visit the manufacturer's website for details on how to reduce interference.
Typically, you should use different frequencies for wireless devices on adjacent computers.
•
Blocked line of sight
—If you are using IR wireless devices, check the line of sight carefully at
the computer, the space between your device and the computer, and the device itself. You might
be dangling a finger or two over the IR eye and cutting off the signal—the equivalent of putting
your finger over the lens on a camera.
•
Serial port IRQ conflicts
—If the wireless mouse is connected to a serial port and it stops
working after you install another add-on card, check for conflicts using the Windows Device