Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
processing. This method is typically used by systems with chipset-integrated audio and by very
low-cost (typically under $50) sound cards.
• DSP-based; a digital signal processor (DSP) performs sound processing in conjunction with the
CPU. This method is used by most sound cards with hardware DSPs.
• DSP with onboard processor; a DSP performs sound processing with its own onboard RISC
processor. This method is used by the Creative Labs CA20K2 (used by the SoundBlaster
Titanium series, Auzen X-Fi Forte and HomeTheater HD). Freeing up the CPU provides for the
fastest system performance, especially with 3D games that use a lot of positional audio.
Advanced Audio Features
Sound cards designed for audiophiles and sound producers typically have additional connectors
designed for their specialized needs, in addition to the standard connectors listed in the previous
section. These might include
•
Aux in
—Provides input for other sound sources, such as a TV tuner card.
•
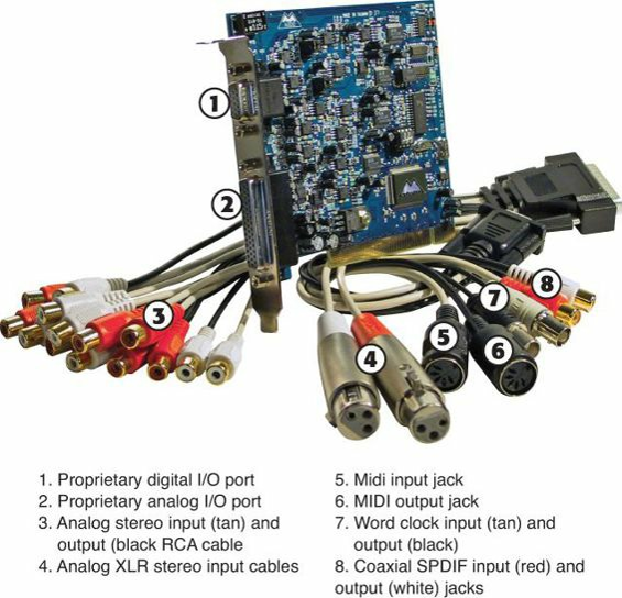
MIDI in and MIDI out
—Older sound cards with game ports (a 15-pin female connector) also
supported MIDI in and MIDI out through adapters that plugged into the game port. With current
high-end sound cards, MIDI ports might be connected via a proprietary breakout cable (see
Figure 13.3
)
or a proprietary I/O port adapter that might occupy a 5.25-inch drive bay or be
placed on a tabletop.