Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
required varies by the resolution and mode. It is governed by the VESA CVT (Coordinated Video
Timings) standard.
CRT Refresh Rate Considerations
Displays with analog connections usually have a range of scan frequencies that they can handle,
which effectively controls the minimum and maximum resolutions that can be displayed. Of the
vertical and horizontal frequencies, for CRT displays the vertical refresh rate is more important
because it controls flicker. A refresh rate that is too low causes CRT screens to flicker, contributing
to eyestrain. The higher the refresh rate you use with a CRT display, the less eyestrain and discomfort
you will experience while staring at the screen.
A
flicker-free refresh rate
is a refresh rate high enough to prevent you from seeing flicker on a CRT.
The flicker-free refresh rate varies with the size and resolution of the monitor setting (larger and
higher resolutions require higher refresh rates) as well as the individual because some people are
more sensitive to it than others. In my experience, a 75Hz refresh rate is the minimum anybody should
use with a CRT, especially at resolutions of 1024×768 and higher. Lower rates produce a noticeable
flicker, which can cause eyestrain, fatigue, and headaches. However, although a 75Hz vertical refresh
rate is sufficient for most, some people require a setting as high as 85Hz before the image is truly
flicker-free. For that reason, 85Hz is considered by VESA to be the optimum refresh rate for CRT
displays. Because a refresh rate that is too high can reduce video performance by making the adapter
work harder to update the image more frequently, I recommend using the lowest refresh rate you are
comfortable with.
Note
CRT manufacturers often used the term
optimal resolution
to refer to the highest resolution a
given CRT monitor supports at the 85Hz VESA standard for flicker-free viewing.
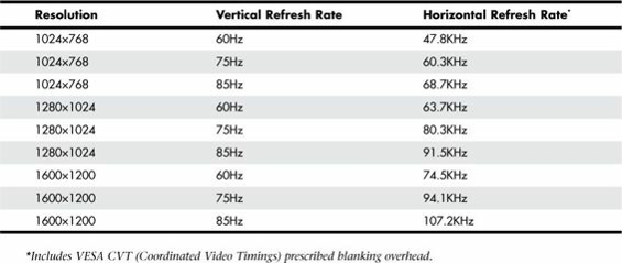
Table 12.21
shows the correlation between resolution and refresh rates. As the resolution and
vertical refresh rate increase, so must the horizontal frequency. The maximum horizontal frequency
supported by the display is the limiting factor when selecting higher refresh rates at a given
resolution.
Table 12.21. Refresh Rates Comparison
For example, let's say you have a CRT display that supports a maximum
horizontal frequency
of