Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
To create a bootable disc, simply follow the directions included with your burning application.
Programs such as Nero and Roxio Media Creator make the creation of bootable discs relatively easy.
LightScribe and LabelFlash
There are two popular direct disc labeling systems, called LightScribe and LabelFlash. Hewlett-
Packard (HP) developed the LightScribe direct disc labeling system in 2005 as a method for labeling
CD (and later, single-layer DVD and, most recently, DL DVD) discs without the need to print labels
or use an inkjet printer equipped to print on CD or DVD media.
The top surface of a LightScribe disc is coated with a reactive dye that changes color when exposed
to laser light. LightScribe uses the recording laser to etch text and graphics on the top surface of
special LightScribe media. After the user records the disc, the user flips the disc over and runs a
LightScribe program to transfer the desired design to the top of the disc. To prevent fading and
surface damage, LightScribe discs should be stored in cases away from light when not in use.
LabelFlash was announced in October 2005 by Yamaha and Fujifilm. LabelFlash is based on the
DiscT@2 (“disk tattoo”) technology originally developed by Yamaha for writing text and graphics
into the unused portion of the data side of a CD-R or DVD R disc. However, LabelFlash can also
write to the top side of media when the user flips the disc, just as with LightScribe. The top side of
LabelFash media is designed to be more resistant to damage and to produce better image quality than
LightScribe because the LabelFlash dye is 0.6mm below the disc surface. However, LabelFlash
labeling only works with specially designed DVD media, while LightScribe labeling is compatible
with specially designed CD as well as DVD media.
The main drawback of either system is that they take up to half an hour or more to fully label a single
disc. Another drawback is that both LightScribe and LabelFlash require drives, media, and software
that support the specific system. For an updated list of products supporting these systems, visit the
LightScribe (
www.lightscribe.com
)
or LabelFlash (
http://labelflash.jp
)
website.
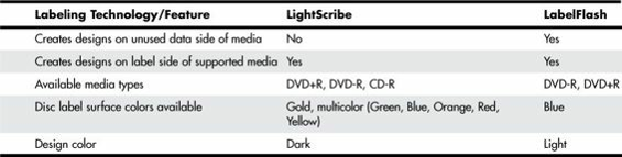
Table 11.26
summarizes the differences between LightScribe and LabelFlash labeling technologies.
Table 11.26. LightScribe and LabelFlash Comparison
Troubleshooting Optical Drives
Failure Reading Any Disc
If your drive fails to read a disc, try the following solutions:
• Check for scratches on the disc data surface.
• Check the drive for dust and dirt; use a cleaning disc.
• Make sure the drive shows up as a working device in System Properties. Check the drive's
power and data cables if the drive is not listed.