Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
as low as 528MB (million bytes). This is due to limitations in both the BIOS and the ATA interface,
which when combined create even further limitations. To understand these limits, you have to look at
the BIOS (software) and ATA (hardware) interfaces together.
Note
In addition to the BIOS/ATA limitations discussed in this section, various operating system
limitations exist. These are described later in this chapter.
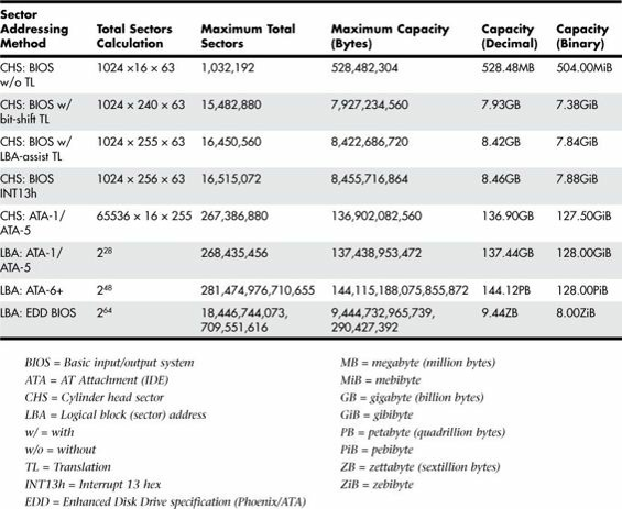
The limitations when dealing with ATA drives are those of the ATA interface as well as the BIOS
interface used to talk to the drive. A summary of the limitations is shown in
Table 7.12
.
Table 7.12. ATA/IDE Capacity Limitations for Various Sector Addressing Methods
This section details the differences between the various sector-addressing methods and the limitations
incurred by using them.
Prefixes for Decimal and Binary Multiples
Many readers are unfamiliar with the MiB (mebibyte), GiB (gibibyte), and so on designations I am
using in this section and throughout the topic. These are part of a standard designed to eliminate
confusion between decimal- and binary-based multiples, especially in computer systems. Standard SI
(system international or metric system) units are based on multiples of 10. This worked well for most
things, but not for computers, which operate in a binary world where most numbers are based on
powers of 2. This has resulted in different meanings being assigned to the same prefix—for example,
1KB (kilobyte) could mean either 1,000 (10
3
) bytes or 1,024 (2
10
) bytes. To eliminate confusion, in