Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
When in Standby mode, the BIOS reduces power consumption by spinning down hard drives and
reducing power to or turning off monitors that comply with Video Electronics Standards Organization
(VESA) and Display Power Management Signaling (DPMS). While in Standby mode, the system can
still respond to external interrupts, such as those from keyboards, mice, fax/modems, or network
adapters. For example, any keyboard or mouse activity brings the system out of Standby mode and
immediately restores power to the monitor.
In most systems, the OS takes over most of the power management settings; in some cases, it can even
override the BIOS settings. This is definitely true if the OS and motherboard both support ACPI.
Boot Menu (Boot Sequence, Order)
The Boot menu is used for setting the boot features and the boot sequence (through menus). If you are
installing an OS from an optical drive or USB flash drive, you'll want to ensure that the optical or
USB drive comes before the hard drive in the boot sequence.
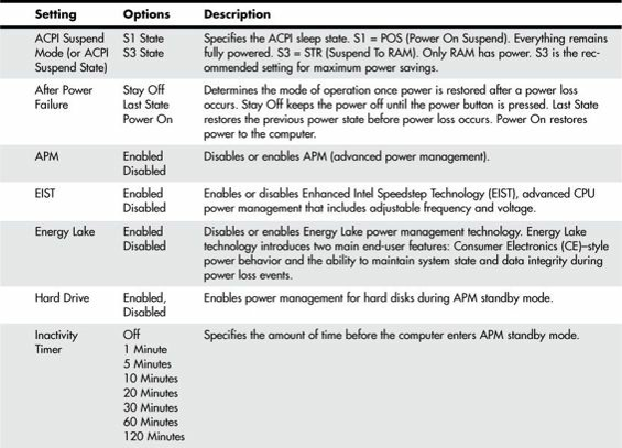
Table 5.22
shows the functions and
settings available on a typical motherboard.