Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
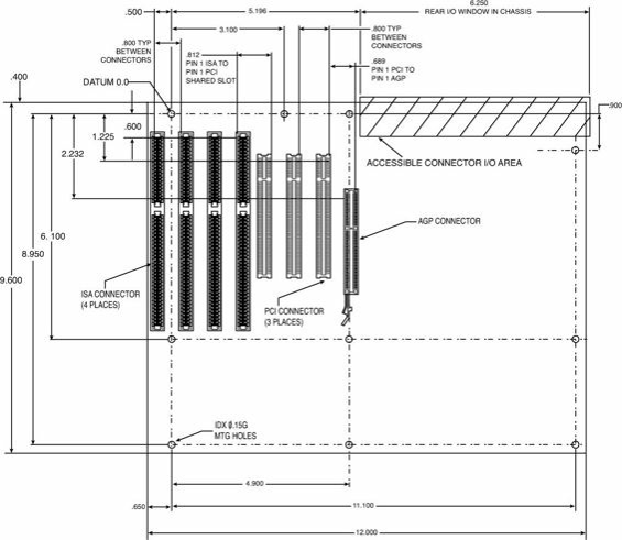
Figure 4.14. ATX specification 2.2 motherboard dimensions. Modern ATX systems no longer
include ISA expansion slots.
Mini-ATX is not an official standard; instead, it is simply referenced as a slightly smaller version of
ATX. In fact, all references to Mini-ATX were removed from the ATX 2.1 and later specifications.
Two smaller official versions of ATX exist, called microATX and FlexATX. They are discussed in
the following sections.
Although the case holes are similar to the Baby-AT case, cases for Baby-AT and ATX are generally
incompatible. The ATX power supply design is identical in physical size to the standard Slimline
power supply used with Baby-AT systems; however, they also use different connectors and supply
different voltages.
The best way to tell whether your system has an ATX-family motherboard design without removing
the lid is to look at the back of the system. Two distinguishing features identify ATX. One is that the
expansion boards plug directly into the motherboard. There is usually no riser card as with LPX and
NLX (except for certain Slimline systems, such as rack-mounted servers), so the slots are usually
perpendicular to the plane of the motherboard. Also, ATX boards have a unique double-high
connector area for all the built-in connectors on the motherboard (see
Figure 4.15
and
Table 4.3
)
.
This is found just to the side of the bus slot area and can be used to easily identify an ATX board.
Note that the colors listed in
Table 4.3
might vary on some systems.