Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
hermetically sealed evacuated enclosure.
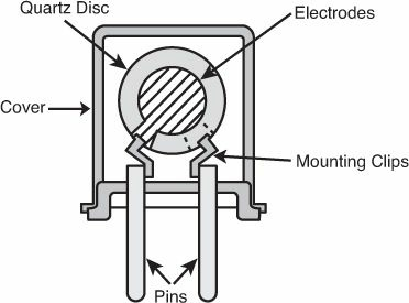
Figure 3.47
shows the interior view of a typical crystal
with a disc-shaped resonator inside. The quartz disc inside has electrodes on each side, allowing
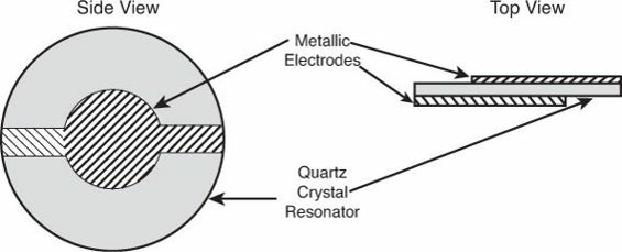
voltage to be applied to the disc. The details are shown in
Figure 3.48
.
Figure 3.47. Figure showing the disc-shaped resonator.
Figure 3.48. Disc-shaped quartz resonator details.
Walter G. Cady was the first to use a quartz crystal to control an electronic oscillator circuit in 1921.
He published his results in 1922, which led to the development of the first crystal-controlled clock by
Warren A. Marrison in 1927. Today, all modern computers have multiple internal oscillators and
clocks, some for controlling bus and processor speeds and at least one for a standard time-of-day
clock.
Modern PC Clocks
A typical PC has at least two crystals on the motherboard; the main crystal controls the speed of the
motherboard and motherboard circuitry, and the other controls the real-time clock (RTC). The main
crystal is always 14.31818MHz (it might be abbreviated as 14.318 or just 14.3), and the RTC crystal
is always 32.768KHz.
Why 14.31818MHz?
The original 1981 vintage IBM PC ran at 4.77MHz, a speed derived by taking a 14.31818MHz
crystal and using a divider circuit to divide the frequency by 3 to get 4.77MHz. Many people