Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
• More accurate branch predictor
• Support for the latest integer instructions FMA4 and F16C
• Improved L1 and L2 cache designs
• Faster clock speeds
Table 3.26
lists the FX processors using Piledriver microarchitecture. These processors use the
Vishera core.
Table 3.26. AMD FX Processors Using Piledriver Microarchitecture
AMD Fusion/HSA (Heterogeneous Systems Architecture) APUs
Fusion was the original name for a variety of AMD mobile, desktop, and server processors with in-
core graphics, which are now classified under the Heterogeneous Systems Architecture (HSA)
designation. AMD refers to these processors as advanced processing units (APUs).
Note
AMD dropped the Fusion name after it was discovered that a Swiss firm, Arctic (originally
Arctic Cooling), had been using Fusion for its power supply products since 2006, hence the
change to the HSA designation.
AMD has released several lines of APUs, including the C-series (primarily for notebooks) and the E-
series (used in notebooks and a few very low-cost desktops). However, the primary product line for
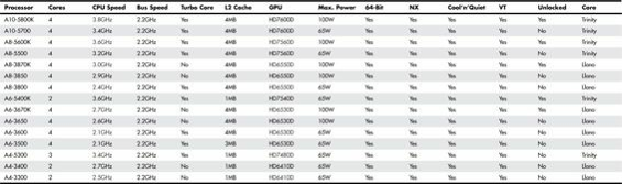
desktops is the A-series, which has used two core designs. The initial A-series designs use the Llano
core, based on Bulldozer, but with no L3 cache, while the second series uses the Trinity core, based
on Piledriver, but again with no L3 cache. The Llano core uses Socket FM1 and includes models with
two, three, or four cores and up to 4MB of L2 cache. The Trinity core uses Socket FM2 and provides
faster clock speeds, better GPU performance, and better thermal management. It also features two to
four cores with up to 4MB of L2 cache.
Table 3.27
compares these processors.
Table 3.27. AMD A-Series Processors
To learn more about AMD APUs (Accelerated Processing Units), see the AMD APUs website at