Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
AMD-K5
The AMD-K5 is a Pentium-compatible processor developed by AMD and available as the PR75,
PR90, PR100, PR120, PR133, PR166, and PR200. Because it is designed to be physically and
functionally compatible, any motherboard that properly supports the Intel Pentium should support the
AMD-K5. However, a BIOS upgrade might be required to properly recognize the AMD-K5. The K5
has the following features:
• 16KB instruction cache, 8KB write-back data cache
• Dynamic execution-branch prediction with speculative execution
• Five-stage, RISC-like pipeline with six parallel functional units
• High-performance floating-point unit
• Pin-selectable clock multiples of 1.5x, 1.75x, and 2x
To learn more about the K5 and AMD's P-Rating system for naming these processors, see Chapter 3
of
Upgrading and Repairing PCs,
19
th
Edition, available in its entirety on the disc packaged with
this topic.
Intel P6 (686) Processors
The P6 (686) processors represent a new generation with features not found in the previous
generation units. The P6 processor family began when the Pentium Pro was released in November
1995. Since then, Intel has released many other P6 chips, all using the same basic P6 core processor
as the Pentium Pro.
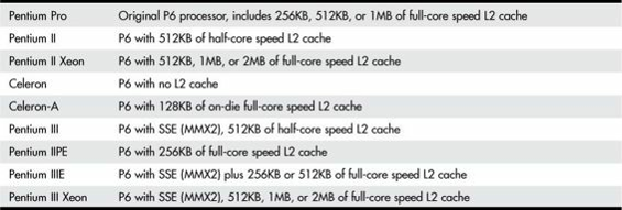
Table 3.13
shows the variations in the P6 family of processors.
Table 3.13. Intel P6 Processor Variations
The main new feature in the fifth-generation Pentium processors was the superscalar architecture, in
which two instruction execution units could execute instructions simultaneously in parallel. Later
fifth-generation chips also added MMX technology to the mix. So then what did Intel add in the sixth
generation to justify calling it a whole new generation of chip? Besides many minor improvements,
the real key features of all sixth-generation processors are Dynamic Execution and the DIB
architecture, plus a greatly improved superscalar design.
Pentium Pro Processors
Intel's successor to the Pentium is called the Pentium Pro. The Pentium Pro was the first chip in the
P6 or sixth-generation processor family. It was introduced in November 1995 and became widely
available in 1996. The chip is a 387-pin unit that resides in Socket 8, so it is not pin compatible with
earlier Pentiums. The chip is unique among processors because it is constructed in a multichip