Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
with a segmented distribution of rtPS connection
with fixed date rate of 1Mbps and the constant
system bandwidth of 4 Mb. Table 2 contains main
system and simulation parameters applied in the
proposed scenario.
As it follows from Table 2, we distribute the
total amount of rtPS load of 1Mb per sec between
3 service connections belonging to ertPS, rtPS
and BE1 service categories in a defined allocation
order, as shown in Table 2. Segmentation of the
rtPS total load into 3 different proportions leads
to a firm system capacity gain achieved while
comparing each allocation scenario throughput
indicators with summary throughput figures,
evaluated during the 1 set of experiments. As il-
lustrated in Figure 5, the best gain ratio of just
fewer than 14% was obtained when most data
were forwarded through rtPS and UGS, addition-
ally exploiting initial UGS of 2 Mb load separation
for 2 UGS connections accounted to 1Mb load
per each. This fact could only support our assump-
tion that the segmented approach would lead to
better performance in comparison with tradi-
tional IEEE 802.16 MAC concept delivery.
Moreover, WRR scheduler first tries to serve
packets from the higher priority layer and assigns
best transmission opportunity for priority-select-
ed packets as well. The less successful indications
with about 9% capacity gain were provided for
the scenario Nº 3.
BE connections were served with no service
guarantee, thus 20% of total rtPS data were de-
livered after satisfying all active connections of
upper priority. The 2
nd
scenario results show no
serious performance gains in comparison with the
approach described above, but it should be noted
that this allocation involves less BE load in com-
parison with the 3
rd
scenario, so it was inherently
unable to outperform the operation of the 1
st
sce-
nario due to effective re-allocation of UGS con-
nection.
Based on our evaluated results we conclude,
that second segmentation model might be a
trade-off solution for delivery video data with
2-enchanced quality layer. A different video dis-
tribution model can be effectively exploited taking
into account the scheduling design. Scheduling
can improve the certain propagation scenario, as
our theoretical concept was experimentally ap-
proved with the simple WRR algorithm to which
no specific properties were added for a selected
service class-oriented priority provision.
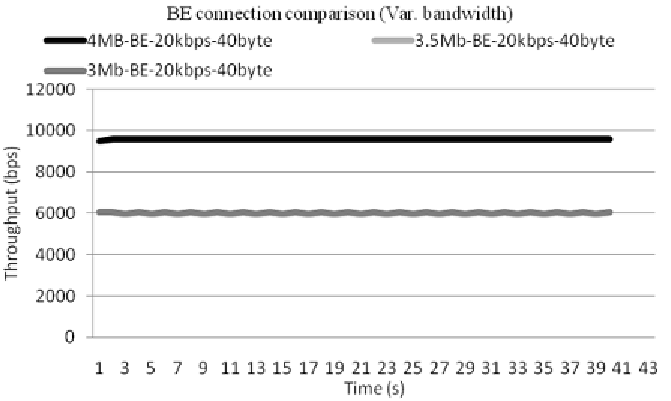
Figure 4. BE comparison for variable system bandwidth
Search WWH ::

Custom Search