Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
software model we optimise segmentation of video
data and verify the developed technique through
case study scenarios, such as medical (e-Health).
In these case studies various QoS-dependant
streams were emulated to quantify the achievable
improvement in the overall network throughput
and to identify critical issues that influence the
performance spatially for the telemedicine appli-
cations. We show that the proposed segmentation
of real-time data flows provides both quantitative
and qualitative system resources utilisation and
identify possibilities for further improvement
by developing a new approach-oriented for the
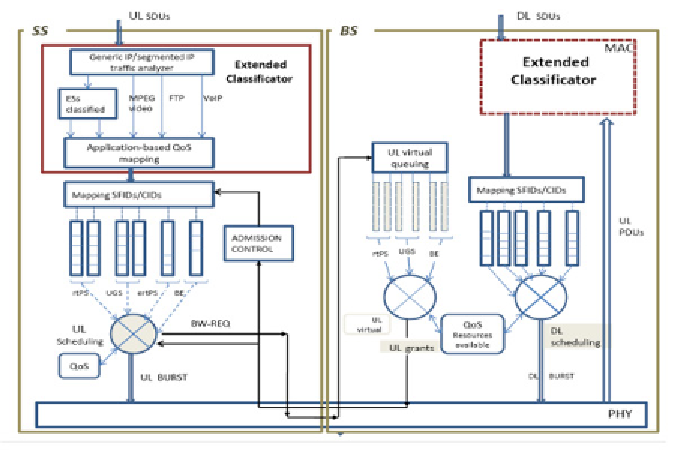
scheduler design (Figure 2).
traffic generally associated with multimedia ap-
plications. With the introduction of IEEE 802.16m
data rates in excess of 75 Mbps in NLOS (Non-
Line-of-sight) conditions are becoming feasible
(Andrews, 2007). The QoS concept incorporated
in the standard assumes the ability to manage
incoming traffic based on application require-
ments, incorporating data with similar demands
into service flows belonging to one out of five
service classes categories adopted in the standard:
•
Unsolicited grant services (UGS),
•
Real time polling service (rtPS),
•
Extended real-time polling service (ertPS),
•
Non real time polling service (nrtPS),
IEEE 802.16 Technology and
Telemedicine Applications
•
Best effort (BE),
IEEE 802.16/WiMAX Standard
which together represent the full set of categories
defining how the application-based data should
be treated. Each category maintains a set of ser-
vice parameters including maximum, minimum
sustained traffic rate, delay and jitter boundaries,
priority function. All the traffic from the upper
IEEE 802.16/WiMAX has been identified as one
of the candidates for next generation IMT- Ad-
vanced systems. It is a cost-effective alternative for
delivering highly intensive, rate/delay-sensitive
Figure 2. A New Distribution Framework for object-based MPEG-4 video in WiMAX
Search WWH ::

Custom Search