Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
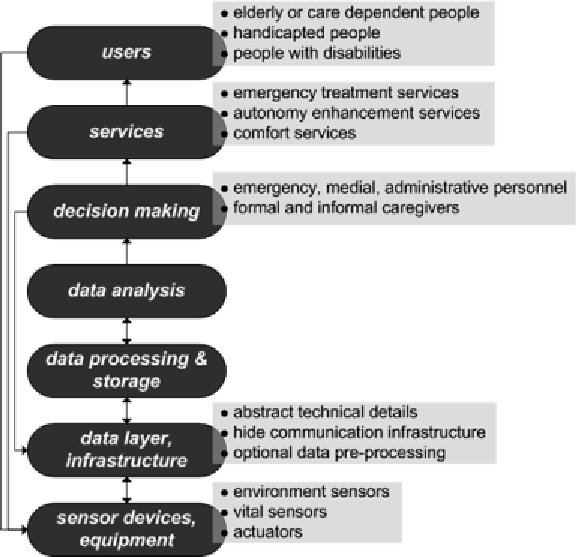
perceiving and storing environmental data by
using a data layer and corresponding communi-
cation infrastructure (e. g. WSNs). Afterwards
the stored and optionally pre-processed data can
be analyzed for further decision making. In case
of a positive match during the decision making
process (a critical situation was detected) available
services are triggered to assist/help the user (e.
g. notify care personnel to look after an elderly
person or simply display a message).
Healthcare systems have, in contrast to AmI
systems, a different structure due to their require-
ments. Healthcare systems are designed to provide
entire and correct information to care or medical
personnel to enable them to take proper actions
in advance (e. g. therapy or rehabilitation patients)
or in case of an emergency. While healthcare ap-
plications mainly focus on acquisition, distribution
and transformation of patient related data, AmI
systems are more technology driven and have to
cope with typically data fusion problems in het-
erogeneous environments.
As already mentioned, there are various ap-
proaches for solving these data fusion problems,
like the JDL Data Fusion Model or Pau's Sensor
Data Fusion Process. Nearly all of these ap-
proaches have in common, that a global picture
of the available and processable data is needed
to provide feasible results, especially to enable
interoperability with other systems, such as health-
care systems. In reality, most of the AmI systems
are a collection of various sensor technologies, that
are enriched by features and additional sensing
technology over the time. In most cases this is due
to their origination domain. Most of them focus
on certain (mostly hardware driven) aspects. The
advantage is that the implementation for defined
use cases can be very accurate, but involves the
risk that the system is not accepted by the user
or less interoperable with systems from related
Figure 3. General architecture of smart systems following (Chan, Esteve, Escriba, & Campo, 2008)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search