Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
•
Continues public/private dialogue that
would lead to a common understanding
and definition of how to foster innovation;
◦
finances
◦
human factor
•
Return
◦
•
What the public/private sector can do to
encourage innovation;
ability to scale
◦
intellectual property
•
Identification of the levers that have an im-
pact on innovation.
◦
price
•
Accessibility
◦
coverage
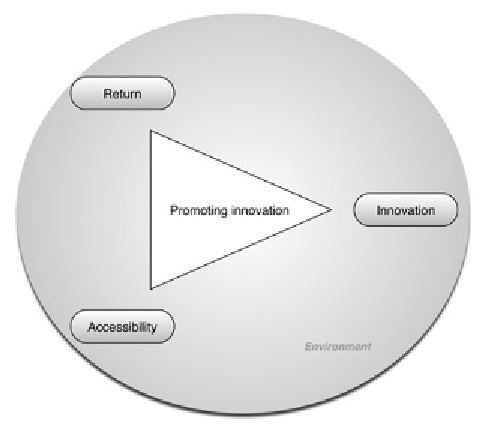
Innovation in health care should be based on a
triangle type of approach (similar to the education
- research - innovation triangle) based on: return,
accessibility and innovation. All of these need to
be considered in the context of the environment
(political and economic).
Figure 8 shows that the innovation is the result
of research and development activities, the process
of discovery and creation. The return signifies
securing a return on the investment done, while
accessibility incurs all the activities that have to
do with the diffusion, distribution and adoption
of the innovative practices. For all these, the set
of levers activating them would be the following:
◦
structure
◦
scalability
Many of the health care innovations come
from developing countries according to Ehrbeck
et al. (2010) because there is a necessity to breed
innovation (in the absence of adequate health,
the providers need to improvise) and because
weaknesses in the system (institutional void)
make them face fewer constraints. Unfortunately,
health care is usually an isolated and un-scalable
type of activity: innovations are not transferred
across systems or sectors. Therefore, identifying
and promoting innovation according to the system
described above is not merely enough. It has to
be replicated elsewhere when successful. There
•
Innovation
◦
planning
Figure 8. The triangle of innovation in health care
Search WWH ::

Custom Search