Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
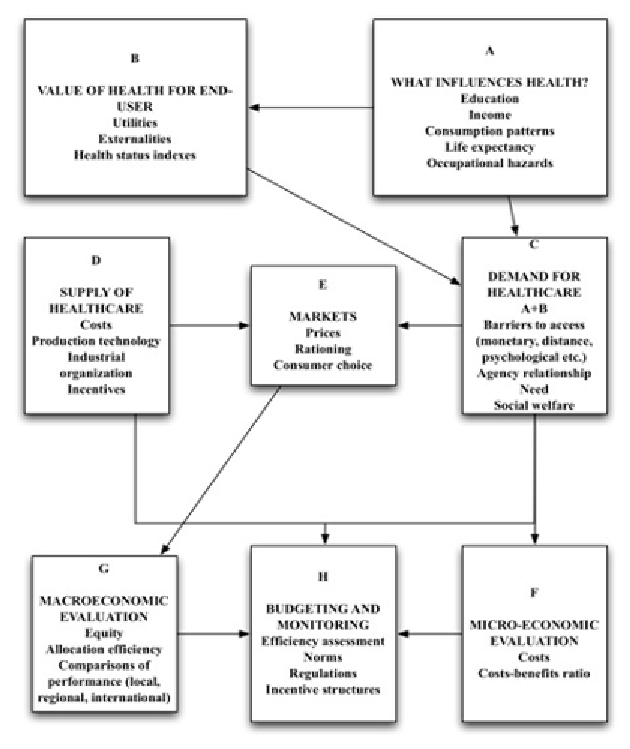
Figure 7. The framework of health economics. (Adapted from Centre for Health Economics, University
of York; Mills, 1988)
As we can see, health economics is concerned
with the analysis of costs, benefits, management
and results of health care. Health economics
draws its inspiration from a number of disciplines
such as finance, insurance, econometrics, labor
economics, public finance, development studies
(
Handbook of Health Economics,
2000).
The research related to health economics has
been surprisingly applied to the health care in
developed countries. Considering the distinction
between positive and normative economics ('what
is' vs. 'what it should be') we can conclude that
health care economics in developing countries is
mainly linked to the normative side of research
(
International perspectives on equity and health:
as seen from the UK,
2002).
The principles of health economics that ap-
ply to developing countries are the same as the
core principles of the main discipline (Mwabu,
2007). Depending on the environment, there
might be a need of adapting these principles to
institutional conditions (or their absence) of de-
veloping economies. These can be (North, 1990;
Williamson, 2000):
Search WWH ::

Custom Search