Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
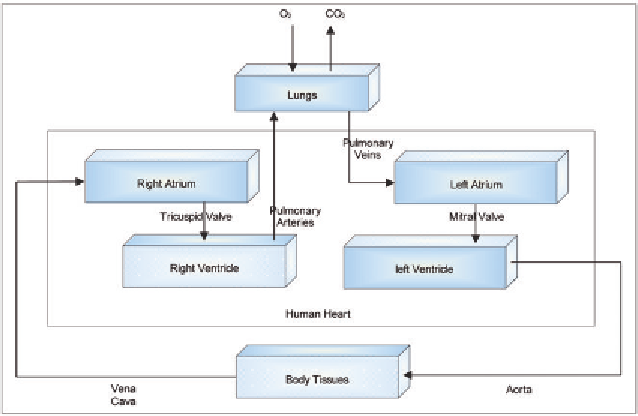
Figure 3. A schematic representation of the human heart operation and anatomy
ventricles. The SA action potential electrically
excites other areas in the ventricles known as the
atrioventrical (AV) nodes. The AV nodes can
discharge impulses but at a rate slower than that
of the SA node. This electrical activity results in
a strong and rapid contraction of the ventricles
which forces blood out of the heart into the blood
vessels.
tion of the ventricular muscles causing a forceful
contraction of the ventricles. The T wave is an
indication of the ventricular repolarization leading
to the relaxation of the ventricular muscles. The
U wave (not always shows on the ECG graph) is
believed to follow the T wave.
ECG-Based Human Identification
ECG Basics
Several proposals (Biel et al., 2001; Israel et al.,
2005; Kyoso & Uchiyama, 2001; Yongjin et al.,
2007; Singh & Gupta, 2009; Sufi, Khalil, & Hu,
2010; Venkatasubramanian & Gupta, 2010) sug-
gested that ECG analysis can, in addition to di-
agnosing heart activity and conditions, accurately
identify the identity of the human subject. These
research proposals relied on the fact that the hu-
man heart exhibits a set of unique physiological
characteristics among different individuals which
can be reflected in the ECG recording. These
characteristics represent a unique signature that
supports the identification task.
A general ECG identification model consists
of two main phases:
ECG is the main tool for assessing the electrical
activity and operation of the heart. It produces a
representation of the variable electrical voltages
generated by the heart during the different phases
of the cardiac cycle. ECG recordings are mainly
analyzed for diagnosing abnormal conditions in
the heart activity. The recordings are obtained by
means of six electrodes placed on the chest and
four placed on the arms and feet. Under normal
conditions, an ECG recording will typically look
like the one presented in Figure 4.
The P wave represents the depolarization of
the atrial muscles leading to their contraction. The
QRS complex mainly results from the depolariza-
Search WWH ::

Custom Search