Database Reference
In-Depth Information
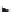
for key transfer. In conventional encryption, as shown in Figure 4.2,
the sender encrypts the data (plaintext) using the encryption key and
the receiver decrypts the encrypted data (ciphertext) into the origi-
nal data (plaintext) using the decryption key. In symmetric encryp-
tion, encryption and decryption keys are identical. Figure 4.3 shows
the public key encryption (asymmetric encryption) in which the
encryption and decryption keys are different. Public key cryptogra-
phy solves the problem of conventional cryptosystems by distributing
the key [45,46]. Table 4.1 shows a comparison between symmetric
encryption and asymmetric encryption.
There are two types of cryptosystems:
• Symmetric (private) key cryptosystems
• Asymmetric (public) key cryptosystems
Sender
Transmission
Receiver
X
e
K
d
Message
Source
Message
destination
Cryptanalyst
(Attacks)
X
X
Encryption
Algorithm
Decryption
Algorithm
Y
Y
K
K
Secret
Key
Secure
Channel
Figure 4.2
Model of symmetric encryption.
X
Cryptanalyst
e source A
e destination B
Message
source
X
Y
X
Encrypt
Decrypt
Destination
K
d
K
e
Key pair
source
Figure 4.3
Asymmetric-key encryption.







































Search WWH ::

Custom Search