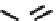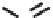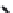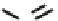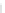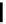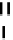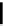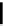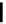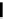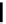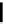Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
NH
2
NH
2
N
N
N
N
O
N
N
HO
HO
O
O
Deoxyadenosine
Deoxycytidine
OH
OH
NH
2
NH
2
NH
2
NH
2
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
O
N
O
N
HO
HO
N
Cl
N
N
Cl
HO
HO
O
O
O
F
HO
O
F
OH
OH
F
OH
OH
Clofarabine
Cladribine
Cytosine arabinoside
(ara-C)
Gemcitabine
NH
2
NH
2
HOH
N
N
N
N
N
N
H
N
O
O
N
N
N
F
HO
N
-O
P
O
HO
O
O
O
O-
HO
OH
OH
Fludaribine
(F-Ara-MP)
OH
Pentostatin
5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine
(Decitabine)
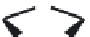
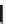
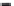
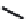
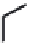
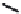
(A)
(B)
FIGURE 5.10
Structures of FDA approved nucleoside analogs. (A) Purine-like nucleosides include fludarabine (9-
b
-D-arabinoside-2-
fluoroadenine), cladribine (2-chlorodeoxyadenosine), clofarabine (2-chloro-9-(2'deoxy-2'-fluoroarabinofuranosyl)adenine), and pentostatin
(2
0
-deoxycoformycin). (B) Pyrimidine-like nucleosides include gemcitabine (2',2'-difluorodeoxycytidine (dFdC)), cytarabine (1-
b
-D-arabi-
nofuranosylcytosine (Ara-C)), and 5-aza-deoxycytidine.
fludarabine as this analog has become the pre-eminent
nucleoside analog used in the chemotherapeutic regimen
for patients with indolent B-cell malignancies and CLL.
Fludarbine has an interesting history that dates back to
early work initially reported in 1969 by Montgomery
and Hewson.
153
These authors were amongst the first to
demonstrate that 2-fluoroadenosine (F-Ado) is resistant
to deamination by adenosine deaminase,
153
a highly
active enzyme that rapidly metabolizes and inactivates
several nucleoside analogs. The ability of 2-fluoroadeno-
sine to inhibit adenosine deaminase predicted that
the nucleoside analog should not undergo rapid degra-
dation. The result of this inhibition would cause
increased cytotoxic effects in clinical settings since there
would be a significant increase in the effective concentra-
tion of the F-ATP. Indeed, Montgomery and Hewson
demonstrated that mice treated with 2-fluoroadenosine
showed a rapid accumulation of various F-Ado nucleo-
tides.
154
Unfortunately, the improved pharmacokinetic
behavior of F-Ado did not confer the expected enhance-
ment in therapeutic activity in this mouse model.
154
However, the improved pharmacokinetic properties of
2-fluoroadenosine suggested that the arabinoside deriva-
tive of 2-fluoroadenine, 9-
b
-D-arabinosyl-2-fluoroade-
nine, would similarly avoid deamination and thus be
effectively converted to the corresponding nucleoside
triphosphate. Indeed, 9-
b
-D-arabinosyl-2-fluoroadenine
(F-ara-A) is one of the most effective nucleoside analogs
used today against hematological disorders.
155
Since
this nucleoside suffers from poor solubility, it is adminis-
tered as the 5
0
-monophosphate and is designated by the
generic name fludarabine or by the trade name Fludara
(Berlex Laboratories, USA).
Pharmacokinetic Features of Purine
Nucleoside Analogs
Figure 5.11
provides a summary of pharmacokinetic
hurdles that must be overcome for most nucleoside
analogs to be pharmacologically active as chain termina-
tors of DNA synthesis. These obstacles primarily include
efficient
cellular
transport
followed by effective