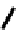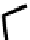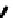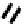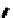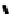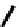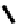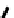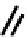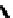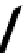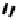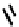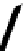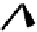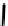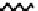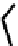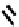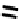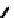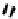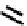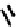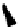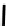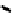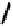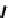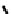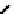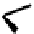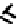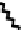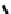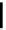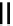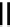Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Thymine
H
3
C
N
O
O
CH
3
(A)
O
6
-Methylguanine
N
Guanine
N
HN
H
3
C
N
N
N
dR
O
N
O
O
NH
2
dR
N
NH
N
N
N
H
3
C
dR
N
dR
NH
2
N
O
H
2
N
NH
2
N
N
N
N
N
dR
NH
2
O
dR
Cytosine
(B)
O
O
H
3
C
O
N
H
3
C
+
N
NH
NH
N
NH
H
2
O
N
NH
2
N
N
NH
2
N
N
N
NH
2
O
O
O
O
+
O
O
O
O
OH
O
H
OH
O
O
O
(C)
N
N
NH
2
H
N
N
NH
2
Cl
Cl
NH
2
O
NH
2
O
O
O
Pt
N
N
N
N
H
2
N
NH
2
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
Pt
NH
2
H
2
N
O
O
O
O
O-
O-
O-
O-
O
O
P
O
O
O
P
O
P
O
O
P
O
O
O
O
O
O
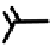
FIGURE 5.7
Representative structures of DNA lesions caused by chemotherapeutic agents. (A) Structure of O
6
-methylguanine caused by
temomozolomide. (B) Structure of apurinic/apyrimidinic (abasic site) lesion caused by enzymatic and spontaneous hydrolysis of glycosidic
bond in DNA. (C) Structure of intrastrand crosslink in DNA caused by cisplatin.
damaged nucleic acid. Provided below are brief summa-
ries explaining the major DNA repair pathways
including mismatch repair (MMR), base excision repair
(BER), nucleotide excision repair (NER), homologous
recombination (HR), and non-homologous end-joining
(NHEJ). We do not provide details regarding the Fan-
coni anemia repair pathway since excellent reviews
have been published by D'Andrea and colleagues.
114,115
THE ROLE OF DNA POLYMERASES
IN DNA REPAIR
DNA Mismatch Repair (MMR)
The MMR pathway is responsible for repairing mis-
paired DNA formed during DNA replication. This
repair pathway is highly conserved amongst organisms