Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
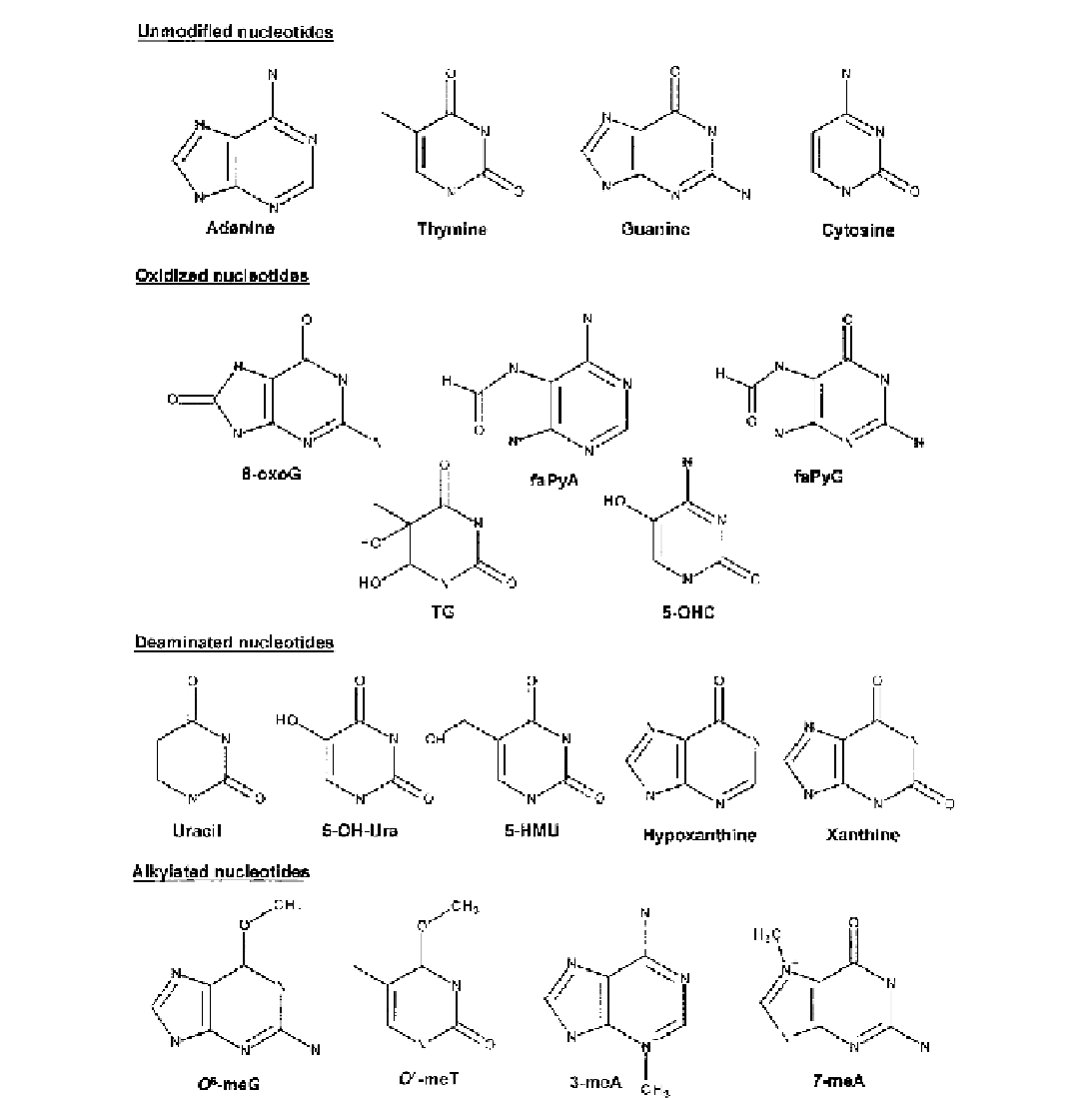
FIGURE 3.1
Chemical structures of the four canonical bases and of the oxidized, deaminated, and alkylated nucleotides processed by the
BER pathway. The various lesions are discussed in the text.
nitrosourea (MNU) (see
Figure 3.1
).
23
O
6
-meG lesions
are mutagenic because they mispair during replication
with thymine, resulting in G:C to A:T transition
mutations. The high cytotoxicity of these lesions
results from the recognition of
O
6
-meG:T mispairs by
the DNA mismatch repair (MMR) pathway, which
attempts to repair them by removing the thymine,
leading to a futile cycle of nucleotide removal and syn-
thesis that generates DNA single- and double-strand
nitrogen mustards, psoralen) alkylating agents used in
anticancer chemotherapies.
21
e
22
DNA bases are
susceptible to different grades of alkylation at all the
exocyclic oxygen and most of the ring nitrogens. The
highly mutagenic and cytotoxic
O
6
-methylguanine
(
O
6
-meG) and O
4
-methylthymine (
O
4
-meT) lesions
mainly result from unimolecular nucleophilic substitu-
tion (S
N
1) by alkylating agents, such as N-methyl-N'-
nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG) and N-methyl-N-