Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
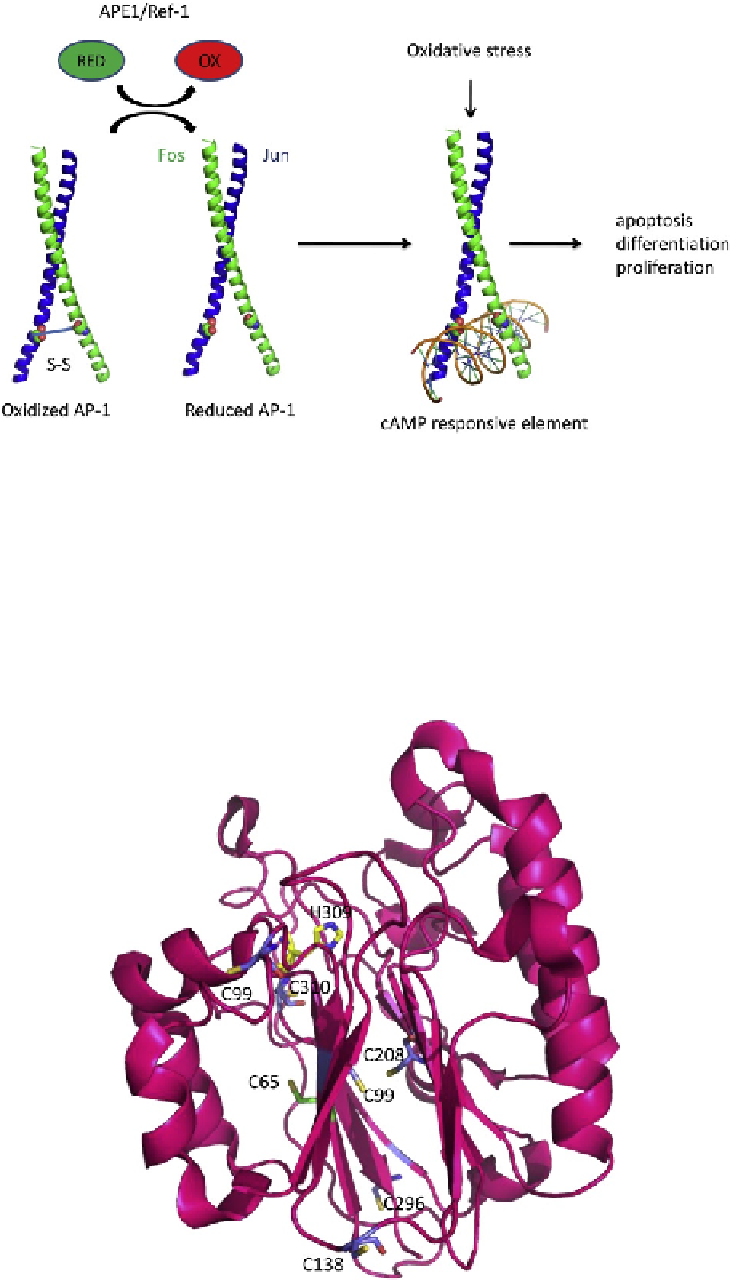
FIGURE 11.3
Oxidized AP-1 (c-Jun/c-Fos) is reduced by the nuclear redox factor, apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease (APE1). A ribbon
rendering is shown of the DNA-binding domains of c-Jun and c-Fos in a putative oxidized state involving a disulfide bond between the Cys
residues within the DNA-binding domain of each protein. Reduction by APE1 greatly stimulated DNA-binding activity of AP-1.
FIGURE 11.6
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease (APE1), shown as a pink ribbon rendering, has seven Cys residues, 65, 93, 99, 138, 208,
296, 310, shown as stick renderings. Cys 65 is shown with carbon atoms in green, oxygens, red, and sulfur, yellow. All other Cys residues are
shown with carbon atoms in blue, oxygen, red, and sulfur, yellow. The redox active Cys residues 65 and 93 are located on opposite sides of the
beta sheet in which they are found. No disulfide bonds are present in the crystal structures reported for APE1. His 309, a critical active site
residue, is shown as a stick model with carbon atoms in yellow, oxygen in red, and nitrogen in blue.