Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
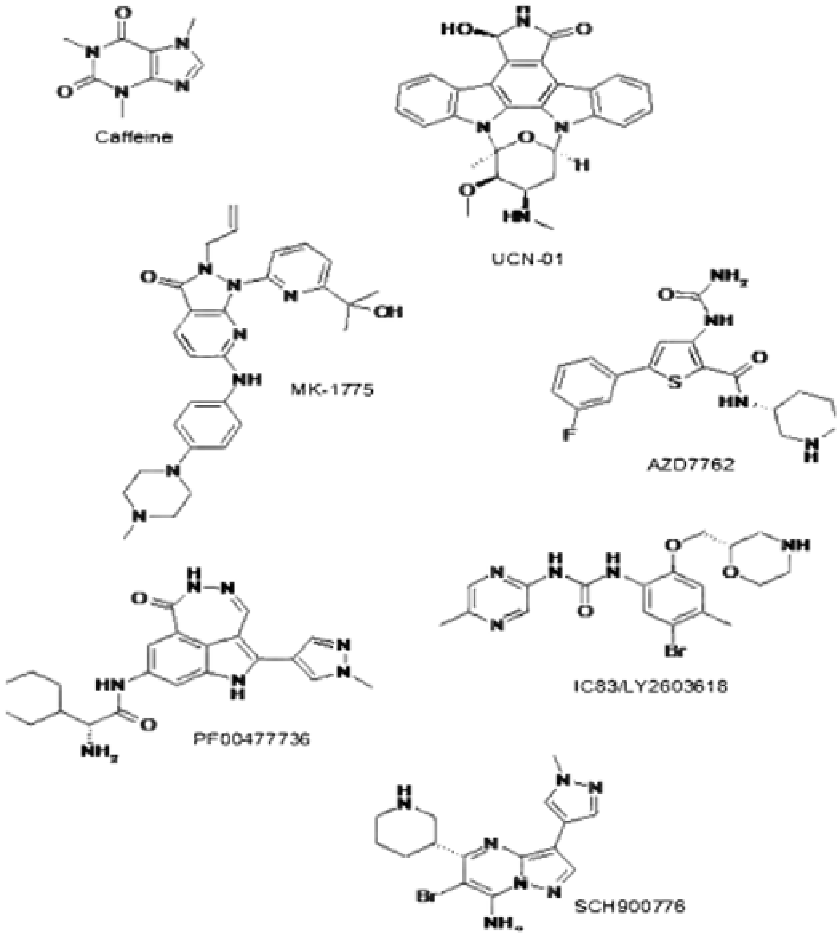
FIGURE 10.2
Chemical structures of Chk and Wee1 kinase inhibitors in clinical trials.
dependent fashion.
81
Furthermore, UCN-01 induces the
expression of the endogenous CDK inhibitors p21 and
p27.
82
Thus, both the direct and indirect inhibition of
CDKs by UCN-01 contributes to a decrease in phosphor-
ylation of the retinoblastoma protein (pRb) that ulti-
mately leads to cell cycle arrest and accumulation of
cells in the G1 phase.
81
Since UCN-01 does not directly interact with DNA in
both cell-free and cellular systems the precise molecular
targets responsible remained obscure until the demon-
stration that apoptosis was mediated through transcrip-
tional suppression of the anti-apoptotic protein, Bcl-xL.
Using two pairs of colon carcinoma cells, it was demon-
strated that the SW48 and LS513 cell lines responded to
UCN-01 treatment by undergoing apoptosis in a
concentration-dependent manner while the HT-29 and
WiDr cell lines were completely resistant. Apoptosis in
LS513 and SW48 cells correlated with the suppression
of Bcl-xL at both the level of mRNA and protein expres-
sion. In contrast, in the apoptosis-resistant cell lines, Bcl-
xL expression was not affected by UCN-01. Further
support for this hypothesis was gained when stable
overexpression of the Bcl-xL protein was shown to
prevent UCN-01-triggered apoptosis.
83,84
More significantly, with regard to the increasing level
of knowledge around DNA damage and repair
processes, UCN-01 provided important insight when it
was found that, at doses too low to have a significant
effect on cell cycle progression (
0.3
m
M), but that were
clinically achievable, the drug could potentiate the effects
<