Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
TABLE 5.1 Power Level of GPS Signals
P
C/A
L1
−
133 dBm
−
130 dBm
−
136 dBm
∗
L2
−
136 dBm
∗
Presently not in L2 frequency.
to generate a uniform power over the surface of the earth, the main beam pattern
of the transmitting antenna is slightly weaker at the center to compensate for the
user at the edge of the beam. The resulting power level versus elevation angle
is shown in Figure 3.10. The maximum power is
−
128 dBm, which occurs at
about 40 degrees. Of course, the receiving antenna pattern also contributes to
the power level of the receiver. Usually the receiving antenna has a higher gain
in the zenith direction. This incorporates the ability of attenuating multipath but
loses gain to signals from lower elevation angles. As discussed in Sections 3.3
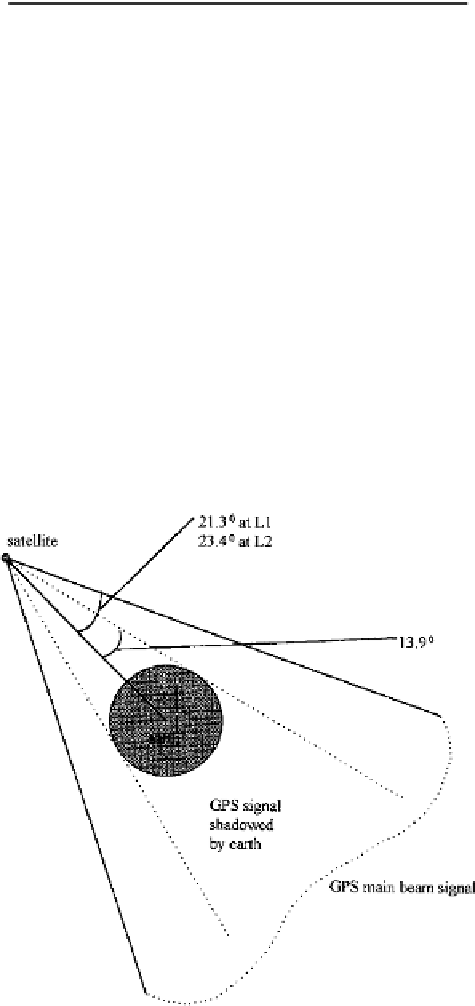
and 3.10, the minimum required beam width of the transmitting antenna to cover
the earth is 13.87 degrees. The beam width of the antenna
(
2
)
is 21.3 degrees,
which is wider than needed to cover the earth as shown in Figure 5.1.
If the user is in an aircraft, as long as it is in the main beam of the GPS signal
and not in the shadow of the earth it can receive the signal. The signals generated
by the satellite transmitting antenna are right-hand polarized. Therefore, the
receiver antenna should be right-hand polarized to achieve maximum efficiency.
FIGURE 5.1
GPS signal main beam.


Search WWH ::

Custom Search