Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
In general, each
C
i
−
1
represents only one single transform. This cascade method
will be used to obtain the earth-centered, earth-fixed system.
4.3 SATELLITE ORBIT FRAME TO EQUATOR FRAME TRANSFORM
(
1,2
)
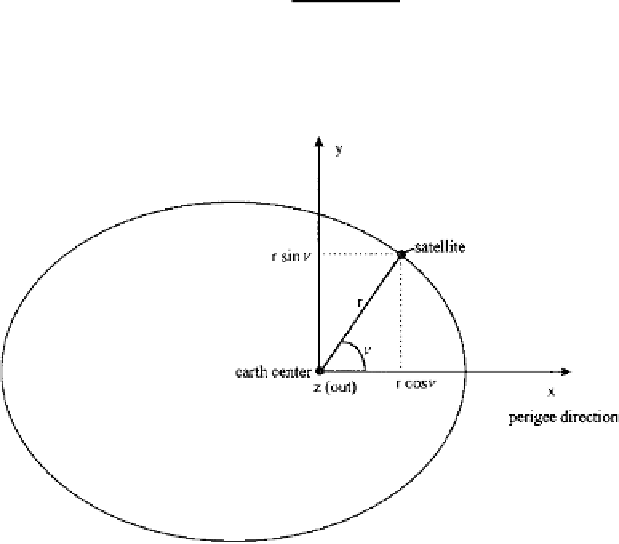
The coordinate system used to describe a satellite in the previous chapter can
be considered as the satellite orbit frame because the center of the earth and
the satellite are all in the same orbit plane. Figure 4.2 shows such a frame, and
the
x
-axis is along the direction of the perigee and the
z
-axis is perpendicular
to the orbit plane. The
y
-axis is perpendicular to the
x
and
z
axes to form a
right-hand coordinate system. The distance
r
from the satellite to the center of
the earth can be obtained from Equation (3.35) as
a
s
(
1
−
e
s
)
1
r
=
(
4
.
8
)
+
e
s
cos
ν
where
a
s
is the semi-major of the satellite orbit,
e
s
is the eccentricity of the
satellite orbit,
ν
is the true anomaly, which can be obtained from previous chapter.
The value of cos
ν
can be obtained from Equation (3.37) as
cos
E
−
e
s
cos
ν
=
(
4
.
9
)
1
−
e
s
cos
E
where
E
is the eccentric anomaly, which can be obtained from Equation (3.30).
FIGURE 4.2
Orbit frame.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search