Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
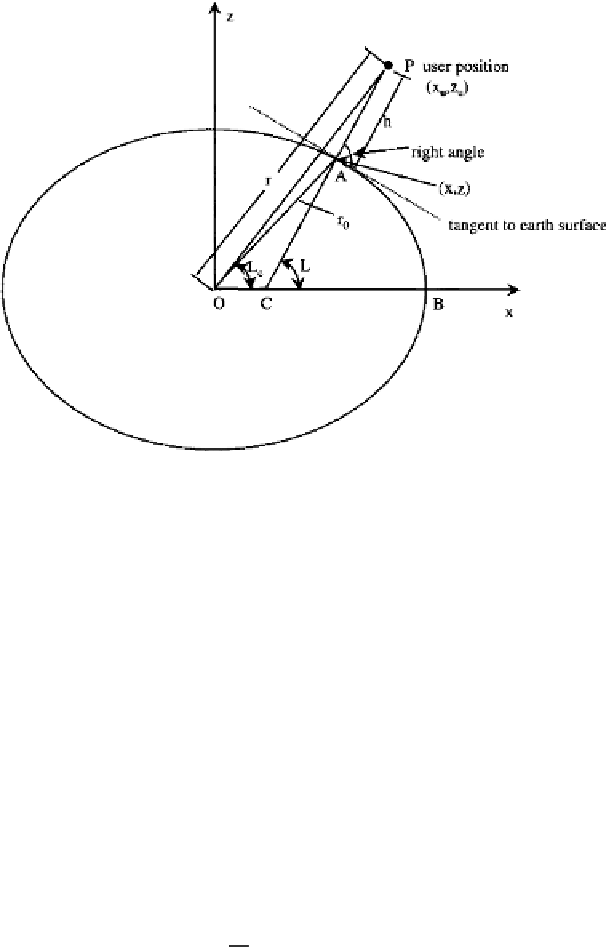
FIGURE 2.5
Geocentric and geodetic latitudes.
L
, the distance
r
0
, and the height
h
. All three quantities are calculated from
approximation methods. Before the actual calculations of the unknowns, let us
introduce some basic relationships in an ellipse.
2.10 BASIC RELATIONSHIPS IN AN ELLIPSE
(
4-7
)
In order to derive the relationships mentioned in the previous section, it is con-
venient to review the basic functions in an ellipse. Figure 2.6 shows an ellipse
which can be used to represent a cross section of the earth passing through the
polar axis.
Let us assume that the semi-major axis is
a
e
, the semi-minor axis is
b
e
,and
the foci are separated by 2
c
e
. The equation of the ellipse is
x
2
a
e
+
z
2
b
e
=
1and
a
e
−
b
e
=
c
e
(2.21)
The eccentricity
e
e
is defined as
a
e
−
1
c
e
a
e
=
b
e
b
e
a
e
=
e
e
=
−
e
e
or
(
2
.
22
)
a
e






Search WWH ::

Custom Search