Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
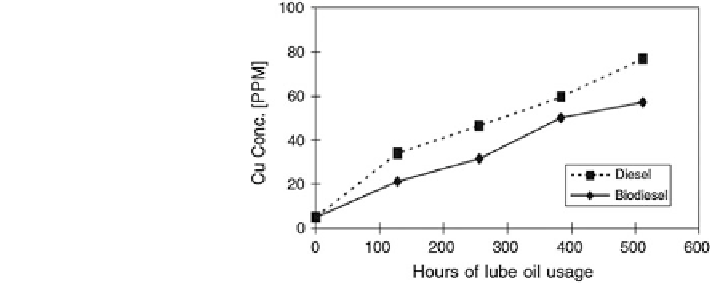
Fig. 8 Copper concentration
as a function of lube oil usage
in the lubricating oil samples
from diesel- and biodiesel
(B20)-fueled engines
(Agarwal
2003
)
A long-term endurance test proved that biodiesel can be successfully used for
partially substituting mineral diesel. This increases the likelihood of biodiesel being
adopted as an alternative fuel for the existing conventional diesel engines without
any major modi
cations in the engine hardware.
5 Summary and Conclusions
Some results showed that any degree of mineral
oil dilution by the tested biodiesels
can reduce the wear protection performance and the viscosity of the engine oil even
at small contaminating amounts. It is expected that study would help understand
interactions of methyl ester components with the engine oil anti
-
wear additives.
Although there are the negative reports in wear, it is expectable that the use of
biodiesel favors to improve durability of engine for biodiesel due to the lower soot
formation and the inherent lubricity, compared with diesel. However, further
detailed investigation of the effect of biodiesel properties on the composition and
property degradation of the lubricating oil as well as engine combustion is required.
These factors are primarily responsible for carbon deposits formation and wear of
engine components and are therefore vital for large-scale implementation of bio-
diesel in transportation engines successfully.
‐
References
Agarwal AK (1999) Performance evaluation and tribological studies on a biodiesel-fuelled
compression ignition engine. PhD thesis, Center for Energy Studies, Indian Institute of
Technology, Delhi, India
Agarwal AK (2003) Lubrication oil tribology of a biodiesel-fuelled compression ignition engine.
In: ASME 2003, internal combustion engine division spring technical conference, American
Society of Mechanical Engineers, pp 751
765
-
Search WWH ::

Custom Search