Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
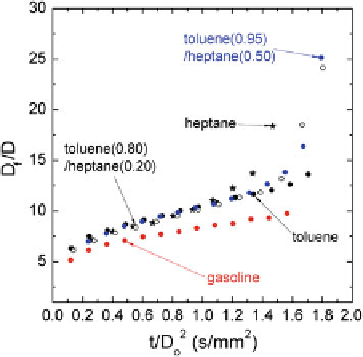
Fig. 15 Comparison of
flame standoff ratio of gasoline with toluene and mixtures of toluene and
heptane (Liu et al.
2012
). The gasoline droplet
fl
flame is consistently closer to the droplet than for
toluene or heptane/toluene mixture droplets, as contrasted with the closer match of the evolution of
droplet diameter for a toluene/heptane mixture with gasoline shown in Fig.
14
fl
an optimization algorithm. Table
3
lists the properties of the surrogates and the
mixture fractions of the components. The 3CS surrogate matched only the DCN and
H/C ratio, but not the TSI or MW. The 4CS surrogate was able to match the four
targets. A test of these surrogates for the con
guration of Fig.
4
was reported by Liu
et al. (
2013b
). Figure
16
shows the results.
It is evident from Fig.
16
that the 3CS and 4CS blends represent jet-A quite well,
with the 4CS being slightly better. This better agreement may be attributed to the
fact that the 4CS matched four targets, while the 3CS, only two. Moreover, the
relative position of the flame to the droplet for the 4CS was in slightly better
agreement with jet-A than the 3CS as shown in Fig.
17
, though as for that both
surrogates were reasonably well correlated with jet-A.
As remarked previously, one of the more attractive features of the spherical
droplet
guration of Fig.
4
a is its one-dimensional gas transport that
facilitates developing a numerical simulation of the burning process that can include
detailed combustion chemistry, unsteady effects, and spectral radiative sub-models.
Armed with this capability, it is possible to use measured combustion properties to
evaluate some of the numerical inputs required for predictions [e.g., modifying the
combustion chemistry to provide a better match between predicted and measured
combustion properties (e.g., Werler et al.
2014
)]. To illustrate the sort of comparative
process that lies at the heart of using a detailed numerical simulation to predict
combustion properties for the spherically symmetric droplet
fl
ame con
guration, we
consider methyl decanoate (MD) droplets burning under conditions that promote
spherical droplet
fl
ame con
flames. MD is sometimes considered a surrogate for biodiesel
derived from rapeseed oil as the feedstock.
fl
Search WWH ::

Custom Search