Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
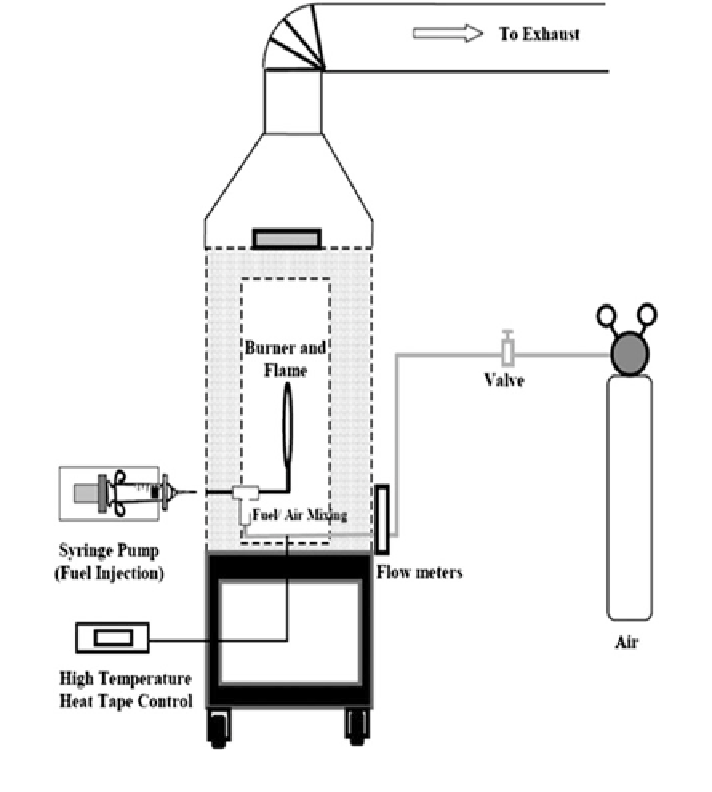
Fig. 1 Diagram of experimental setup
vaporize the injected fuel and low enough to prevent coking in the feed lines. The
heated line was long enough (230 cm) to ascertain that the liquid fuel was com-
pletely vaporized in the air stream before exiting the burner. The liquid fuel was
delivered to the heated air (supplied from a compressed air tank) through a high-
temperature silica-based septum with a 50-cm
3
-capacity syringe attached to a syr-
inge pump. A periodic examination of the tube walls indicated the absence of any
coking. Also, experiments with an air/fuel ratio analyzer indicated that the entire
mass
flow of liquid fuel injected into the heated air stream exited the burner in
vapor state (based on the carbon balance). The volume
fl
fl
flow rate of air was mon-
itored using a calibrated rotameter. The fuel
air mixture was ignited at the exit of
-
the burner with an external propane pilot
fl
flame which was removed after ignition.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search