Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
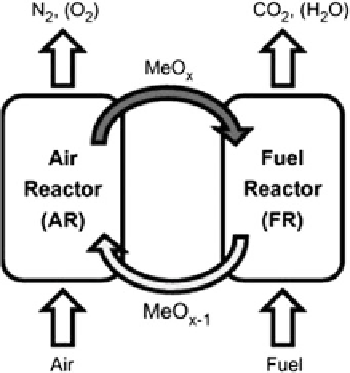
Fig. 7 The concept of
chemical-looping combustion
(CLC) is based on the
application of fluidized bed
technology (Penthor et al.
2014
)
5 Conclusions
It can be seen that the
fluidized bed technology is a very useful technology which
has been applied in a wide range of power generation applications. Fuels as dif-
ferent as coals, biomass, sludges, and waste with different qualities can be utilized
well in
fl
fluidized beds.
Scale-up has been continued and recently successfully demonstrated in the 600
MWe size range. High ef
fl
ciencies can be achieved using supercritical and ultra-
supercritical steam conditions in large-scale CFB boilers. Those units are based on
coal.
Biomass is utilized using
fl
fluidized bed technology as well. Biomass can be
added to large-scale
fluidized bed boilers; however, biomass is typically utilized in
smaller scale. Those biomass combustors operate usually in a size range from about
30 to about 130 MWth. On the other hand, there are a few large-scale biomass-
based FBC in operation. The world
fl
is largest at present is the Polaniec CFB boiler in
Poland with a capacity of 447 MWth.
The
'
fluidized bed technology is very suitable to utilize wastes, for example,
assorted MSW, RDF, and even plastics. Typically, the FBCs are in a smaller size
range, which extend from 40 to 140 MWth, similar to those FBCs which are based
on biomass utilization.
Novel concepts and successful demonstrations using
fl
fluidized bed technology
are already on the market or under development, for example, the steam gasi
fl
cation
of biomass wherein the syngas produced is rich in H
2
and CO which can be used for
synthesis or in gas engines or oxyfuel combustion which produces a CO
2
-rich
fl
ue
gas which signi
cantly helps in CO
2
removal or in chemical-looping combustion
(CLC).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search