Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
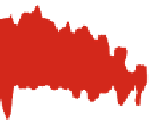
Fig. 5 C
2
vibrational
temperature pro
le during
premixed HITAC. Fuel: coal
gas
(K)
900
1300
800
900
1200
1000
1000
1100
1200
1100
1000
1000
1000
900
900
800
4 m
Thermo - couple temperature
700
(K)
1450
1400
1350
1200
1200
1300
1400
1200
1200
1250
1200
1200
1200
1200
1200
1000
1150
1200
1200
1100
1200
1200
1200
1200
1050
1200
1200
1200
1000
2.2 m
C
2
vibrational temperature
Premixed flame Exposure time 0.01[s]
3.1 Applications of Planer Laser-Induced Fluorescence
Spectroscopy (PLIF)
Spontaneous emission spectroscopy and visualization is a simple method as descri-
bed above and suitable for on-site measurements of industrial combustion system.
For more scienti
c research, this has such disadvantages as the measured image is
constructed from integrated emission intensity of radiation along the view line and
also dependent on the combustion temperature. Laser-induced Fluorescence Spec-
troscopy (LIF) is a powerful tool to overcome these problems though the systems are
more sophisticated and expensive. When Q-branch lines of vibrational spectra are
selected for the excitation lines, the temperature dependence is minimized. The
excitation laser beam is made in a plane and induces cross-sectional
fl
fluorescence in
combustion
uorescence
(PLIF). In this chapter, two application will be described: 2D monitoring of OH for
fl
flames. This method is called as planar laser-induced
fl































































































































































































































































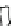













































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search