Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
={
}
- For buildings, Height
low, high, medium, very high, not very low, …
={
}
- For people, Height
tall, short, medium, very tall, more or less short, …
•
}
Although the number of terms in a Linguistic Variable can be large, usually it is
comprised between 5 and 9 (7
LV
=
Speed, is Speed
={
fast, slow, very slow, more or less fast, not fast, …
2) since, in a lot of cases, less than 5 shades is poor
and more than 9 is excessive. Anyway in a good number of applications there only
appear the three terms
P
,
aP
, and
MP
.
Usually, in the applications, the variables range in the set of real numbers and,
because of this, the predicate
P
acts in some interval of the real line. For example,
the linguistic variable 'Temperature' in the interval between
±
−
10, and 50 degrees Celsius, is often represented by only the three terms
μ
cold
, μ
hot
,
μ
w
arm
, with warm
=
not cold and not hot.
Analogously, 'Height' for people, can be represented in
[
,
]
0
2
meters by the lin-
guistic variable with the four terms
μ
tall
, μ
short
, μ
v
er y shor t
, μ
more or less tall
in the
following figure,
1.5.1 Fuzzy Partition
It is sometimes useful in the applications that, once ordered in some sequence, the
fuzzy sets in a linguistic variable
LV
={
μ
0
, μ
1
,...,μ
n
}
do form what is called a
fuzzy partition
(or a unit's partition), that is, verifying
n
0
μ
j
(
x
)
=
1
,
∀
x
∈
X
.
j
=
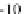





















Search WWH ::

Custom Search