Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Of special importance for the applications are the probabilities defined in the real
line
R
F = B
the so-called
Borel's algebra
, given by all the unions, comple-
ments and intersections of the open, closed, semi-open, and semi-closed intervals of
R
, with
. Then, if
A
∈ B
, the probability of
A
is
defined
by the Lebesgue-Stieltjes integral
p
(
A
)
=
dP
=
μ
A
(
x
)
dx
=
E
(μ
A
),
A
R
that is, as the mathematical expectation of
μ
A
. Then, if
μ
∈[
0
,
1
]
R
is Borel-
measurable, it can be analogously defined
p
(μ)
=
E
(μ)
=
μ(
d
)
dx
R
Obviously,
p
(μ
0
)
=
E
(μ
0
)
=
0,
p
(μ
1
)
=
E
(μ
1
)
=
1, and if
μ
˃
follows
p
(μ)
p
(˃)
. In addition, with
μ
·
˃
=
min
ⓦ
(μ
×
˃)
,
μ
+
˃
=
max
ⓦ
(μ
×
˃)
,itis
p
(μ
+
˃)
+
p
(μ
·
˃)
=
p
(μ)
+
p
(˃),
that implies: If
μ
·
˃
=
μ
0
, then
p
(μ
+
˃)
=
p
(μ)
+
p
(˃)
.
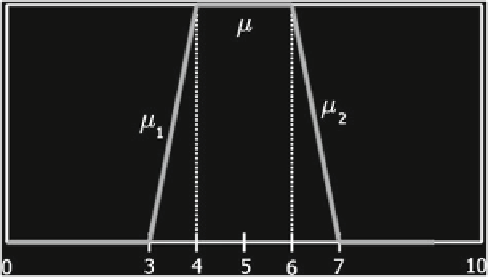
Example 7.8.2
Which is the probability of the fuzzy set
μ
(fuzzy event) given by
Solution
+
+
10
·
p
(μ)
=
]
μ
dx
=
]
μ
dx
=
]
μ
1
dx
1
dx
]
μ
2
dx
=
[
0
,
10
[
3
,
7
[
3
,
4
[
4
,
6
]
[
6
,
7
+
+
1
1
2
3
10
2
]
(
x
−
3
)
dx
]
(
7
−
x
)
dx
=
2
+
2
+
=
3. Then
p
(μ)
=
=
0
.
3.
[
3
,
4
[
6
,
7


Search WWH ::

Custom Search