Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Proof
A
C
A
C
=
(ˀ(
), ˀ(
))
=
(
(
),
(
)),
1
max
A
, and 0
min
N
A
N
A
C
A
C
follows that if
N
(
A
)>
0, then
N
(
)
=
0, and
ˀ(
A
)
=
1
−
N
(
)
=
1. If
A
C
A
C
ˀ(
A
)<
1, then
ˀ(
)
=
1 and
N
(
A
)
=
1
−
ˀ(
)
=
0
Remark 7.5.8
Although the proof will not be presented, let's show the following
important notice.
In the case X is finite, for any possibility measure
ˀ
it exists a (non
X
unique!) fuzzy set
μ
∈[
0
,
1
]
with Sup
μ
=
1
such that
ˀ
=
ˀ
μ
.
In the finite case,
all possibility measures come from possibility distributions.
7.6 Examples
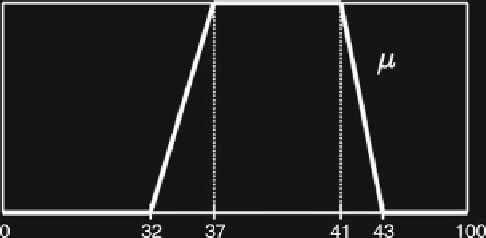
Example 7.6.1
On the age of a person
p
it is only available the incomplete informa-
tion given by
1. 37
Age
(
p
)
41
2. It is neither
Age
(
p
)
32, nor
Age
(
p
)
43.
What can be said about the possibility and the necessity of “
Age
(
p
)
42”,
“
Age
(
p
)
40”, and “
Age
(
p
)
33”?
Solution
The available incomplete information can be represented by the following possi-
bility distribution
μ
:
Hence,
•
ˀ
μ
(
Age
(
p
)
42
)
=
ˀ
μ
(
[
42
,
100
]
)
=
Sup
min
(μ(
x
), μ
[
42
,
100
]
(
x
))
=
x
∈[
0
,
100
]
Sup
μ(
x
)
=
μ(
42
)
:∈
(
0
,
1
)
. Hence
N
ˀ
μ
(
Age
(
p
)
42
)
=
0.
x
∈[
42
,
100
]
The value
μ(
42
)
can be computed as follows. The segment between
(
41
,
1
)
and
(
43
,
0
)
, verifies
Search WWH ::

Custom Search