Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
{5}
μ
Q
∗
μ
{
5
}
μ
Q
∗
NC
μ
{
5
}
μ
{
5
}
it is clear that
is not comparable with
(
), and that
μ
Q
∗
=
1
−
μ
Q
∗
. Hence,
μ
Q
∗
∈
Conj
(
{
μ
{
5
}
}
)
, and namely
μ
Q
∗
∈
Sp
(
{
μ
{
5
}
}
).
1
Notice that
μ
Q
∗
(
5
)
=
4
=
1.
Example
. Rule, “If
x
is big, then
y
is very big”, with
X
=
Y
=[
0
,
10
]
and the
observation “
x
is constantly equal to 0
.
8” for all
x
∈[
0
,
1
]
. Taking
y
2
μ
B
(
x
)
=
x
,μ
v
B
(
y
)
=
,
J
(
a
,
b
)
=
min
(
a
,
b
)
(Mamdani),
follows
y
2
μ
Q
∗
(
y
)
=
min
(μ
P
∗
(
0
.
8
), μ
v
B
(
y
))
=
min
(
0
.
8
,
).
Graphically,
=
√
0
since
y
2
μ
P
∗
=
μ
Q
∗
=
=
0
.
8 means
y
.
8. Hence, it is
μ
0
=
μ
Q
∗
μ
P
∗
, and
1
.
Notice that this second example contains the observation that the input is a con-
stant.
Last Remark
For any continuous t-norm
T
, the function
−
μ
Q
∗
, that imply
μ
Q
∗
∈
Conj
(
{
μ
P
∗
}
)
, and namely
μ
Q
∗
∈
Hyp
(
{
μ
P
∗
}
)
μ
:
Y
ₒ[
0
,
1
]
, defined by
μ(
)
=
(μ
P
∗
(
),
(μ
P
(
), μ
Q
(
))),
∀
∈
,
y
Sup
x
∈
X
T
x
J
x
y
y
Y
does verify




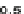









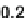








Search WWH ::

Custom Search