Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
1
,
if
y
=
y
0
μ
Q
(
y
)
=
μ
{
y
0
}
(
y
)
=
y
0
,
0
,
if
y
=
and the output is
J
(μ
P
(
x
0
),
),
=
1
if
y
y
0
μ
Q
∗
(
y
)
=
J
(μ
P
(
x
0
), μ
{
y
0
}
(
y
))
=
J
(μ
P
(
x
0
),
0
),
if
y
=
y
0
.
Example 3.4.1
Take
X
, and the rule
'If x is small, then y is
big'
, with the observation that
'x is big'
and
J
=[
0
,
1
]
,
Y
=[
0
,
10
]
(
a
,
b
)
=
max
(
1
−
a
,
b
)
. With the
y
10
,μ
P
∗
(
membership functions
μ
P
(
x
)
=
1
−
x
,μ
Q
(
y
)
=
x
)
=
x
,itresults
y
10
))
=
y
10
))
=
μ
Q
∗
(
y
)
=
sup
W
(
x
,
max
(
x
,
W
(
1
,
max
(
1
,
1
,
x
∈[
0
,
1
]
μ
Q
∗
=
μ
1
, that means
Q
∗
=
or,
all.
Example 3.4.2
With the same rule of last example and the input
x
0
=
0
.
5, it is
y
10
)),
∀
μ
Q
∗
(
y
)
=
max
(
0
.
5
,
max
(
0
.
5
,
y
∈[
0
,
1
]
graphically,
Q*
Example 3.4.3
With the rule 'If x is small, then
y
=
8', and the input
x
=
0
.
5, is
1
,
if
y
=
8
μ
Q
∗
(
y
)
=
max
(
0
.
5
,μ
{
8
}
(
y
))
=
8
,
0
.
5
,
if
y
=
graphically,




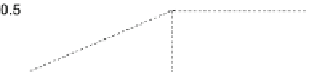













Search WWH ::

Custom Search