Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
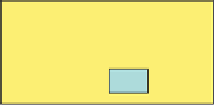
Test room
Position of experimenter
Inlets of
sampling lines
Action area
APS
FMPS
Table
NAS
Sampling lines
CPC
Door
Position of video camera
FIGURE 12.13
Schematic setup of test room and instruments. (Courtesy of IUTA.)
insulation stone wool without and with aerogel as a nanoporous additive to improve
the insulation capabilities. The test setup chosen was similar to the one of Bello et al.
(2009a) by using a test room of 25 m³ without forced ventilation instead of an enclo-
sure. This was done to simulate working with building materials in a private home
(Figure 12.13).
To assess the number size distribution of the particles in the test room an FMPS,
APS, and a CPC were employed, if possible outside of the test chamber to avoid
particle emission from the measurement devices. Particles were also collected with
an ESP for subsequent identification of released particles.
Five holes were drilled into the composites with a 10-mm drill bit for wooden
material within a 30-s time interval. To determine the particle contribution from the
drilling machine itself, a blank test, that is, running the drill for 30 s without load,
was conducted. The results showed that particle emissions by drilling are dominated
by nanoscale particles. These particles appear independent of the material under
investigation and can be attributed to motor emissions. A significant influence of
the nanoadditive on the emission in this size class was not observed and the total
number of additional particles in the investigated size range is low when compared
to ambient or workplace particle number concentrations. Nevertheless, fragments of
the aerogel were identified on SEM samples.
Drilling generates airborne particles in nanoscale range, but often stemming from
the drilling machine. They also appear to be not influenced by the presence of nano-
material in the material.
The general test setups for drilling testing are not completely comparable to each
other and no comparisons between them have been made. Still basic investigations
on the process itself and the correct test setup seem to be necessary.
12.2.7 C
utting
and
s
aWing
Cutting/sawing is a relatively low speed mechanical process with a limited contact
area to the material. It is used to derive specific forms and pieces from composite





Search WWH ::

Custom Search