Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
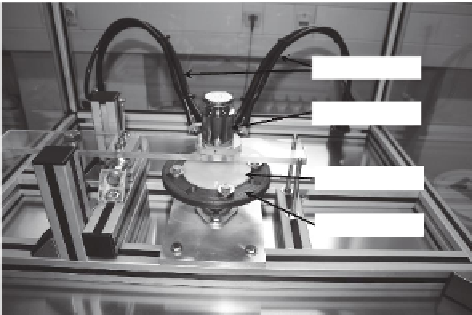
Within the nanoGEM project, IUTA developed an experimental setup to inves-
tigate possible nanoparticle release during sanding of various composite materials
using defined but adjustable test settings. Therefore, a test rig was constructed where
the electrical engine was placed outside of an isolated chamber, simultaneously
allowing particle measurements during the sanding procedure (Figure 12.5). The
chamber is flushed with HEPA filtered air through two inlets and sealed dustproof to
ensure low background particle concentrations. The test object is mounted to a rotat-
ing disk in the middle of the flow channel. The external motor moves the sanding
plate by means of a magnetic clutch. The rotational speed and thus the velocity of the
sample are adjustable. A stationary stamp fixes the sanding paper.
The sampling of the airborne sanding dust was conducted using conductive tubes.
The background measurement in the chamber served as reference for each exam-
ined material. Two different sandpapers (201 and 46.2 µm grit size) were used, the
Sampling lines
Weight
Sample
Rotating plate
(a)
FMPS
WELAS
(APS)
CPC
Weight
1 kg
Counter
weight
Extension holder
Stamp
Abrasive paper
Abrasion
test object
Abrasion plate
(Rotating disc)
(b)
FIGURE 12.5
Example of a test setup to investigate particle release by sanding. (Courtesy
of IUTA, nanoGEM.)












Search WWH ::

Custom Search