Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Release
characteristics
Release process
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
2
1 0
100
1000
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
2
Changing
parameters
1 0
100
1000
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
2
1 0
100
1000
FIGURE 12.2
Influence of changing parameters during the release process on particle
release.
This chapter focuses on the methods of testing and characterizing various
mechanical and thermal release processes along the lifecycles of a nanocomposite.
The possibility and need for standardized release test methods will be discussed.
Other relevant environmental release processes are described by Nowak (2014) in
Chapter 15 and Nguyen et al. (2014) in Chapter 14 of this topic. The accompanying
Chapter 13 by Brouwer et al. (2014) in this topic presents the current knowledge
on the results of release investigations linked to exposure-related measurements
at workplaces. For further information on measurement techniques and analytical
methods employed for the characterization of released particles the reader is referred
to Chapters 1, 2, and 11 by Izak-Nau and Voetz (2014), Asbach (2014), and Asbach
et al. (2014) all in this topic.
12.2 RELEASE DUE TO MECHANICAL PROCESSES
Mechanical processes, mainly sheer forces, lead to stress, and release of nanomateri-
als may occur along the whole lifecycle of a nanocomposite. Some of the processes
discussed as follows may take place in more than one step of the lifecycle, for exam-
ple, abrasion. This slow and relatively soft process may occur during processing, use,
and recycling or during environmental transport of nanocomposites (fragments) in
natural waters; other processes such as drilling occur only during further processing
of nanocomposite materials. Overall, all of the processes described in this section
are potentially relevant for the release of nanomaterials into the environment either
suspended in air or in liquids, mainly water. The definitions of the processes are
based on those discussed in a report by Canady et al. (2013).











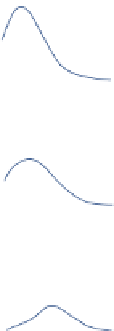

Search WWH ::

Custom Search