Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Nanopharmaceuticals
Nanosized
drug particles
e.g. Nanocrystals
Carrier systems
e.g. Liposomes
Polymeric NP
Dendrimers, etc.
New therapy
options
in particular for
biopharmaceutics
Stability
Targeting
Non-invasive
application
Reformulation
of existing
formulations
protection
against
degradation
• Passive:
EPR, ElVIS, etc.
• active:
surface functional
groups
Capability to
overcome
biological barriers
Altered
pharmako-
kinetik
profile
Diminished
toxicological
profile
Enhanced
water
solubility
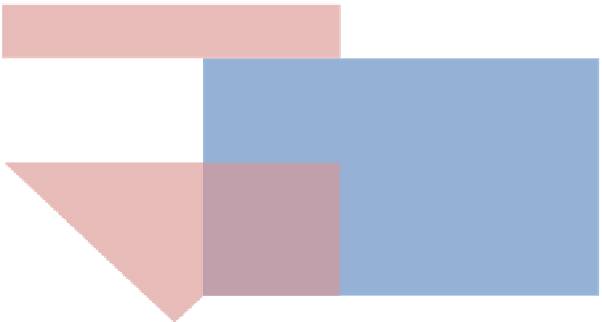
FIGURE 6.2
Chances for nanopharmaceuticals—an overview.
sirolimus was developed to overcome this issue. Nevertheless, bioavailability was
still only 14% and a strong influence of high-fat food on drug uptake could be
observed (Lampen et al. 1998; Zimmerman et al. 1999). Besides that, the solution
had an unpleasant taste and was unstable at room temperature; thus had to be stored
refrigerated. Wyeth successfully developed a tablet formulation, which is compa-
rable to the oral solution in terms of therapeutic issues. Moreover, this new for-
mulation provides stability at room temperature and improves palatability (Mathew
et al. 2006). The new formulation is based on a wet media-based milling technique
(Nanocrystal Technology) (Liversidge and Cundy 1995; Liversidge 1992).
6.5.2.2 Abraxane
®
(Paclitaxel)
With the disruption of microtubule function, taxanes represent an important class of
antitumor agents (Schiff and Horwitz 1980; Rowinsky, Cazenave, and Donehower
1990; Ringel and Horwitz 1991). The clinical advances are limited by the highly
hydrophobic character of the molecules, causing poor water solubility and hence
poor bioavailability. For example, the conventional solvent-based paclitaxel formu-
lation (Taxol
®
) contains high amounts of Cremophor EL
®
as surfactant to improve
the solubility of paclitaxel. This formulation requires a long infusion period and is
associated with severe hypersensitivity reactions. Premedication with corticosteroids
and antihistamines is therefore required (Subramaniam et al. 2003). Additionally,
due to the formation of micelles in the plasma compartment that entrap paclitaxel,
formulations with Cremophor EL show nonlinear pharmacokinetics, meaning the
given dose of paclitaxel is not linear to the plasma drug concentration (Sparreboom
et al. 1999). Abraxane, a new Cremor EL
®
-free formulation of paclitaxel, is based on
the nanoparticle albumin-bound (nab
TM
) technology to improve solubility of pacli-
taxel and decrease side effects of older formulations (Hawkins, Soon-Shiong, and
Search WWH ::

Custom Search