Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
SiO
2
Phosphate
SiO
2
Amino
24h
1h
2h
5h
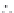
Total: 104
14000
12000
10000
8000
6000
4000
2000
0
Total: 53
SiO
2
naked
Total: 131
19
SiO
2
PEG
58
Total: 152
15
82
46
31
14
SiO
2
Phosphate
SiO
2
Amino
Medium
SiO
2
naked
SiO
2
PEG
27
74
(a)
(b)
17
39
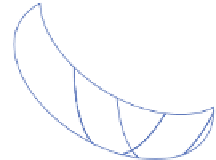
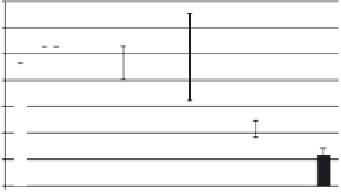
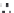
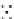
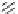
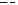
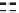
FIGURE 4.2
Analysis of protein corona for four different variants of SiO
2
. (a) Four differ-
ent variants of SiO
2
nanoparticles (naked, PEG, phosphate, amino) have been characterized
in
situ
in DMEM cell culture medium containing 10% FCS with respect to protein corona forma-
tion. The nanoparticles have been dispersed by stirring the nanoparticles in the test medium
for the indicated period of time. After that the nanoparticles were centrifuged in a table top
centrifuge at 18,400 ×
g
, the resulting pellet was thoroughly resuspended and washed three
times in PBS. Adsorbed proteins were then eluted with Laemmli buffer and subsequently
analyzed with 1D-SDS-PAGE. Protein bands were visualized by Coomassie staining and
were semiquantitatively assessed with ImageLabTM Software (BioRad, Munich, Germany).
Gels were normalized via five different marker bands that were present on all gels in the same
amount. Total bound protein amounts were calculated by summing all band intensities of the
respective lanes taking into account the normalization. (b) The protein corona of the same
nanoparticle types was analyzed with 2D gel electrophoresis after eluting the corona with 2D
buffer containing 7 M urea. The gels were stained with a ruthenium-based fluorescence dye
and analyzed with Delta 2D
TM
(Decodon, Greifswald, Germany). Spots which were statisti-
cally significantly enriched in the protein corona of the particles compared to control (only
DMEM with 10% FCS, no nanoparticles) were taken into account (at least 1.5 fold higher
than control,
p
< 0.05). The Venn diagram shows the overlap in protein species for the differ-
ent types of SiO
2
nanoparticles.
chain length is rather short (PEG 400), the protein adsorption is only time delayed
but not completely avoided. Thus, after longer incubation times the differences
between SiO
2
naked and SiO
2
PEG are only marginal. Furthermore 2D gel analysis
was applied to separate the protein species of the protein corona (Figure 4.2b). With
this approach it could be shown that a substantial amount of spots is similar for all
tested nanoparticles but these spots are also present in the negative control without
any nanoparticles. This background is caused by the presence of serum contain-
ing aggregates that are formed even without the presence of nanoparticles. But for
each nanoparticle type we could identify unique protein species that are specifi-
cally enriched in comparison to the no nanoparticle control. Those proteins are spe-
cifically trapped on nanoparticle surfaces and are truly protein corona components.
Each nanoparticle type displays a unique pattern with protein species that are unique
to that particular nanoparticle type. It could be confirmed that indeed there is a large






















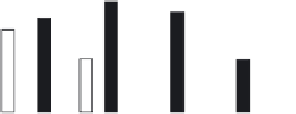





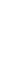

































Search WWH ::

Custom Search